Phenanthrene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, is a precursor for numerous derivatives, offering unique properties and applications across various industries. Here are some common derivatives of phenanthrene, along with their uses:
1. Phenanthrenequinone
Phenanthrenequinone is a phenanthrene derivative commonly known as 9,10-phenanthrenequinone. It is a yellow crystalline solid with a molecular formula C14H8O2. Due to its unique chemical properties, phenanthrenequinone has several important uses across various industries.
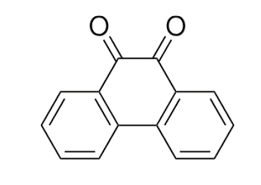
Uses of phenanthrenequinone:
- Chemical Synthesis: Used in producing dyes, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.
- Photography: Enhances image development in photographic chemicals.
- Batteries: These are used in redox flow batteries for energy storage.
- Chemical Analysis: Acts as a reagent for detection in analytical chemistry.
- Medicinal Chemistry: Investigated for potential therapeutic applications, including anticancer and antimicrobial properties.
2. 9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene
9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene, also known as tetrahydrophenanthrene, is a derivative of phenanthrene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. It is characterized by its saturated structure, containing a fully hydrogenated ring system compared to phenanthrene’s aromatic ring structure.
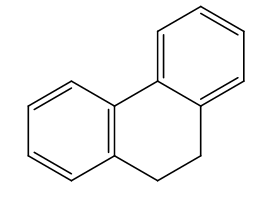
Uses of 9,10-Dihydrophenanthrene:
- Chemical Synthesis: Intermediate for producing pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals.
- Materials Science: Enhances properties of organic materials for electronic devices.
- Research: Used as a model compound for studying chemical reactions.
- Fuel Additive: Potential application as a fuel additive to improve combustion properties.
3. Phenanthrene-9,10-dione
Phenanthrene-9,10-dione, commonly known as anthraquinone, is a prominent aromatic compound with a molecular structure consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is important in various industries and scientific fields due to its diverse chemical properties and wide-ranging applications.
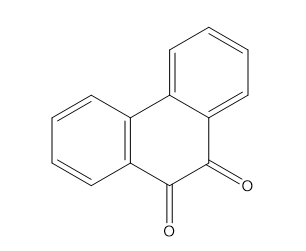
Uses of Phenanthrene-9,10-dione:
- Chemical Synthesis: A precursor in producing dyes, pigments, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals.
- Dyes and Pigments: Provides vibrant colors for textiles, printing, and dyeing industries.
- Pharmaceuticals: Studied for laxative, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects, with potential in cancer treatment.
- Chemical Intermediates: Key in organic synthesis for creating complex molecules.
- Photography: Enhances light sensitivity in photographic materials.
- Battery Technology: Investigated for high-performance lithium-ion batteries.
4. Phenanthrene-3,4-dicarboxylic acid
Phenanthrene-3,4-dicarboxylic acid is a chemical compound important in various fields due to its unique structure and versatile properties. With two carboxylic acid functional groups attached to the phenanthrene backbone, this compound offers various applications in chemical synthesis, polymer, materials science, medicinal, and analytical chemistry.
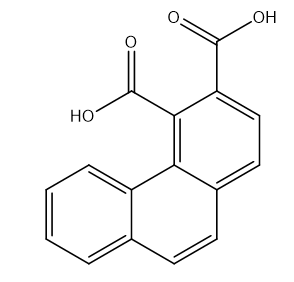
Uses of Phenanthrene-3,4-dicarboxylic acid:
- Chemical Synthesis: Used as a building block for pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals.
- Polymer Chemistry: Forms high-performance polymers for coatings, adhesives, and fibers.
- Materials Science: Utilized in metal-organic frameworks for gas storage and catalysis.
- Medicinal Chemistry: Investigated for potential therapeutic properties.
- Analytical Chemistry: Employed as a reference standard for compound detection and quantification.
5. 9-Chlorophenanthrene
9-Chlorophenanthrene is a compound derived from phenanthrene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. With a chlorine atom substituted at the 9th position of the phenanthrene ring system, this compound exhibits unique chemical properties that make it valuable in various applications.
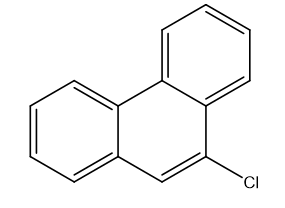
Uses of 9-Chlorophenanthrene:
- Chemical Synthesis: A building block for pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals.
- Materials Science: Synthesis of functional materials like organic semiconductors.
- Analytical Chemistry: Reference standard for compound detection.
- Research: Tool for studying reaction mechanisms and molecular transformations.
Phenanthrene derivatives have various uses in organic synthesis, materials science, pharmaceuticals, and research, which can lead to innovative applications and advancements in chemistry and technology.




