Meta Description
Learn about sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle salt)—its preparation, properties, and uses in medicine, Fehling’s test, and food processing. Discover its laxative and antacid benefits!
Introduction
Sodium potassium tartrate (NaKC₄H₄O₆·4H₂O), commonly known as Rochelle salt, is a double salt of tartaric acid widely used in medicine, analytical chemistry, and industry. This compound serves as a laxative, an ingredient in Fehling’s solution, and an antacid. Additionally, it plays an important role in electroplating, food processing, and pharmaceutical applications. Understanding the properties of sodium potassium tartrate, its preparation methods, and its medicinal benefits is essential for various scientific and medical fields.
This article explores the preparation of sodium potassium tartrate, its physical and chemical properties, medicinal uses, and potential side effects.
How is sodium potassium tartrate (Rochelle salt) prepared? (Step-by-Step)
Sodium potassium tartrate is synthesized through a reaction between tartaric acid, potassium carbonate, and sodium carbonate in aqueous solution.
Step 1: Reaction of Tartaric Acid with Potassium Carbonate
Tartaric acid reacts with potassium carbonate (K₂CO₃) to form potassium tartrate.
C₄H₆O₆ + K₂CO₃ → K₂C₄H₄O₆ + CO₂ + H₂O
Step 2: Addition of Sodium Carbonate
Potassium tartrate is then treated with sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃) to form sodium potassium tartrate.
K₂C₄H₄O₆ + Na₂CO₃ + H₂O → NaKC₄H₄O₆·4H₂O
The resulting compound crystallizes as a tetrahydrate.
Properties of Sodium Potassium Tartrate
Chemical Properties:
Molecular Formula: NaKC₄H₄O₆·4H₂O
Molecular Weight: 282.2 g/mol
Solubility: Soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol
pH: Mildly alkaline
Optical Activity: Rotates plane-polarized light
Physical Properties:
Appearance: Colorless to white crystalline powder
Taste: Slightly saline
Melting Point: Decomposes at 75°C–80°C
Alkaline Nature: Mildly alkaline in aqueous solutions
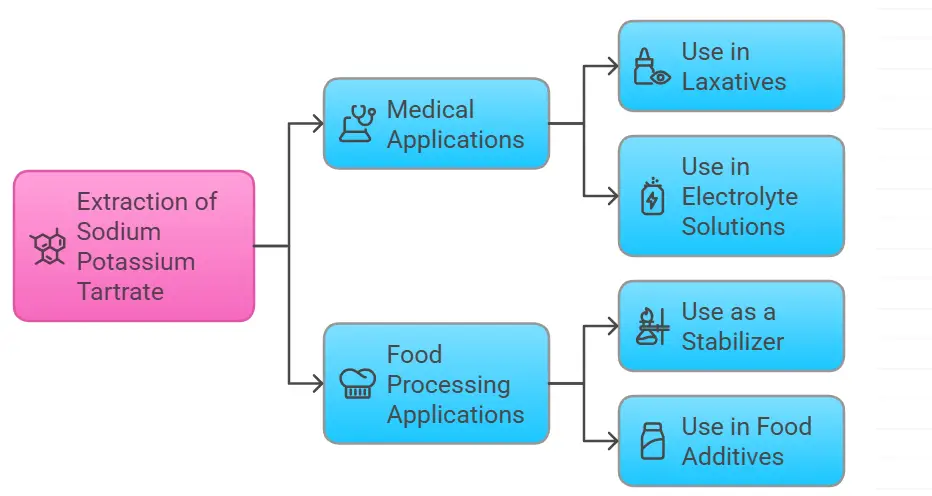
Top Medicinal Uses of Sodium Potassium Tartrate (Rochelle Salt) in Healthcare
1. Laxative Action
- – Used as a mild saline purgative for treating constipation.
- – Works by drawing water into the intestines, promoting bowel movement.
2. Component of Fehling’s Solution
- – Essential in Fehling’s test, which detects reducing sugars like glucose and fructose.
- – Acts as a complexing agent to keep copper(II) ions in solution.
3. Antacid Properties
- – Due to its mild alkalinity, it is used in antacid formulations to relieve acidity.
4. Electroplating and Pharmaceuticals
- – Used in metal electroplating to enhance surface coating.
- – Found in pharmaceutical formulations as a stabilizing agent.
Side Effects of sodium potassium tartrate
While sodium potassium tartrate is generally safe, excessive intake may cause:
- 1. Diarrhea and Dehydration: Overuse as a laxative can lead to fluid loss.
- 2. Electrolyte Imbalance: Prolonged use may disrupt sodium and potassium levels.
- 3. Gastrointestinal discomfort: can cause nausea, bloating, or cramps in sensitive individuals.
- 4. Allergic reactions: Rare cases of hypersensitivity may occur.
Precaution
Always consult a healthcare provider before using sodium potassium tartrate, especially if you are pregnant, have kidney disorders, or suffer from chronic gastrointestinal conditions.
Conclusion
Sodium potassium tartrate is a versatile chemical compound with significant applications in medicine, chemistry, and industry. Its preparation, properties, and medicinal uses make it a valuable ingredient in pharmaceuticals and analytical chemistry.
Have you used sodium potassium tartrate in your industry? Share your experience in the comments!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is sodium potassium tartrate used for?
Answer: It is used as a laxative, an analytical reagent, and a complexing agent in metal ion detection.
2. Why is sodium potassium tartrate called Rochelle salt?
Answer: It was first prepared in Rochelle, France, giving it the common name Rochelle salt.
3. What is the function of sodium potassium tartrate in Fehling’s solution?
Answer: It acts as a complexing agent, keeping copper(II) ions in solution, which react with reducing sugars.
4. Is sodium potassium tartrate safe for consumption?
Answer: In small amounts, it is safe, but excessive intake may cause diarrhea and gastrointestinal discomfort.
5. How is sodium potassium tartrate different from potassium tartrate?
Answer: Potassium tartrate contains only potassium ions, while sodium potassium tartrate contains both sodium and potassium ions.




