Meta Description
Learn about antidotes, their types, and their crucial role in poison treatment. Discover how these life-saving agents neutralize toxins and prevent severe poisoning complications.
Introduction
An antidote is a critical component of poison treatment, designed to counteract the harmful effects of toxins in the body. These substances work through different mechanisms, such as neutralizing toxins, blocking their absorption, or accelerating their elimination. Antidotes are essential in emergency poisoning care, where rapid administration can save lives and prevent severe complications. Whether for snake bites, drug overdoses, or chemical exposures, understanding antidote uses can help ensure timely and effective treatment. In this article, we explore the different types of antidotes, their mechanisms, and their importance in managing poisoning cases.
Definition of Antidote
An antidote is a specific agent used to neutralize or mitigate the toxic effects of poisons, drugs, or chemicals. It acts through various mechanisms such as:
- Chemical Neutralization (Directly reacting with the poison)
- Competitive Inhibition (Blocking toxin absorption or receptor binding)
- Metabolic Conversion (Enhancing toxin metabolism for elimination)
- Physiological Counteraction (Opposing the toxic effects on the body)
Types of Antidotes
Antidotes are categorized based on their mechanism of action:
1. Chemical Antidotes
These antidotes react chemically with the toxin to neutralize its effects.
Example: Activated charcoal (binds to poisons to prevent absorption).
2. Pharmacological (Receptor) Antidotes
These antidotes block or compete with toxins at receptor sites.
Example: Naloxone (opioid overdose antidote, blocks opioid receptors).
3. Metabolic Antidotes
These antidotes enhance the metabolism or elimination of the toxin.
Example: Ethanol/Fomepizole (treatment for methanol/ethylene glycol poisoning).
4. Mechanical Antidotes
These antidotes physically remove the poison from the body.
Example: Gastric lavage (stomach pumping) for drug overdoses.
Importance of Antidotes in Poison Treatment
1. Rapid Toxicity Reversal: Antidotes act quickly to neutralize poisons and prevent organ damage.
2. Life-Saving Emergency Treatment: Essential in acute poisoning cases (e.g., snake bites, opioid overdose, heavy metal poisoning).
3. Reducing Long-Term Health Effects: Early administration prevents neurological damage, kidney failure, or respiratory distress.
4. Essential in Industrial and Household Poisoning Cases: Antidotes are crucial for accidental ingestion of toxic chemicals, insecticides, and heavy metals.
5. Enhancing Drug Safety in Medicine: Used in overdose management of common drugs like paracetamol, benzodiazepines, and opioids.
Commonly Used Antidotes and Their Applications
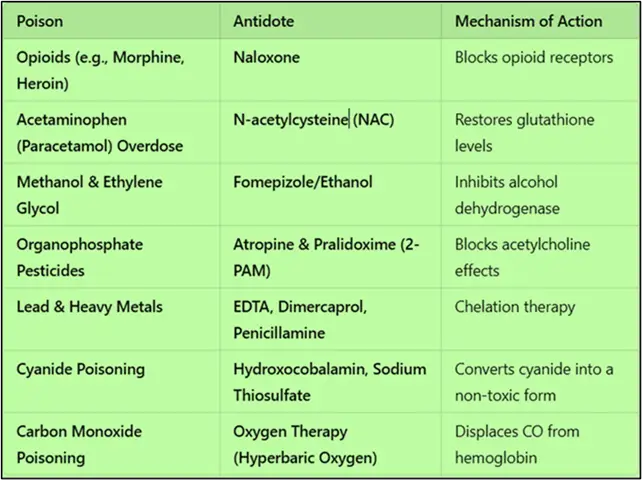
Figure: antidote-poison-treatment
Conclusion
Antidotes are critical tools in poison management, helping to neutralize toxins, prevent complications, and save lives. Their effectiveness depends on early diagnosis, proper administration, and understanding their mechanisms. Knowing the right antidote for a specific poison can significantly improve patient outcomes in medical emergencies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is an antidote in poison treatment?
Answer: An antidote is a substance used in poison treatment to neutralize toxins, prevent damage, and counteract the harmful effects of poisons in the body.
2. How do antidotes work in emergency poisoning care?
Answer: Antidotes work by blocking toxins, enhancing metabolism for quicker elimination, or reversing toxic effects. Some antidotes, like naloxone for opioid overdose, act immediately, saving lives in emergency poisoning care.
3. What are common antidotes used for poison treatment?
Answer: Naloxone is Used for opioid overdose
Activated Charcoal: Prevents poison absorption in the stomach
N-acetylcysteine (NAC): Treats paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning
Atropine: Counteracts pesticide poisoning
Hydroxycobalamin: Neutralizes cyanide poisoning
4. Can all poisons be treated with an antidote?
Answer: No, some poisons have no specific antidote. In such cases, doctors use supportive care, like IV fluids, oxygen therapy, or dialysis, to manage symptoms and remove toxins from the body.
5. How quickly should an antidote be administered?
Answer: Immediate administration is crucial. In cases like cyanide or opioid poisoning, antidotes must be given within minutes to prevent life-threatening complications.
Have you or someone you know ever needed an antidote? Share your experience in the comments below!




