Structure:
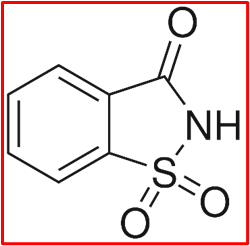
IUPAC Name: 2H-1λ6,2-benzothiazol-1,1,3-trione
Molecular Formula: C7H5NO3S
Properties:
- Saccharin, an artificial sweetener, is remarkably sweet, surpassing sucrose 300–400 times. However, it carries a bitter or metallic aftertaste, especially in higher concentrations.
- Saccharin exhibits heat stability and remains inert, avoiding chemical reactions with other food ingredients.
- It is water-insoluble, but its sodium salt is water-soluble.
Uses:
1. Food and Beverages: Saccharin is commonly used as a low-calorie artificial sweetener in various food and beverage products, providing sweetness without adding significant calories.
2. Tabletop Sweeteners: They are employed in tabletop sweeteners for individuals seeking a sugar-free or low-calorie alternative for sweetening drinks and foods.
3. Diabetic-Friendly Products: Saccharin is often included in diabetic-friendly and reduced-sugar products, catering to individuals with diabetes or those managing their sugar intake.
4. Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceuticals, saccharin may be present in medications and healthcare products to enhance taste without contributing to caloric content.
5. Cosmetics: In cosmetics and personal care items, saccharin may impart sweetness to flavoured products like lip balms and toothpaste.
6. Industrial Applications: Beyond the food and beverage industry, saccharin finds applications in industrial processes, such as electroplating a brightener.