Introduction
Accuracy is a fundamental parameter in pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring that the measured values of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients closely match their true values. It is a key component of method validation, directly impacting drug safety, efficacy, and regulatory compliance.
In this post, we will explore the concept of accuracy, its importance, types, and real-world examples in pharmaceutical analysis.
What is Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis?
Accuracy in pharmaceutical analysis refers to the closeness of the measured result to the actual value. It reflects how well an analytical method measures the true concentration of an analyte in a sample without systematic errors.
Accuracy is often expressed as the percentage of recovery by analyzing a known amount of standard (spiked sample) and comparing it with the actual amount present.
Importance of Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Regulatory Compliance: Regulatory agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and ICH require pharmaceutical products to meet stringent accuracy standards.
- Patient Safety: Inaccurate dosage determination can lead to under-dosing or overdosing, affecting patient health.
- Quality Assurance: Ensures that drugs contain the intended amount of API and excipients.
- Consistency in Manufacturing: Supports batch-to-batch consistency in pharmaceutical production.
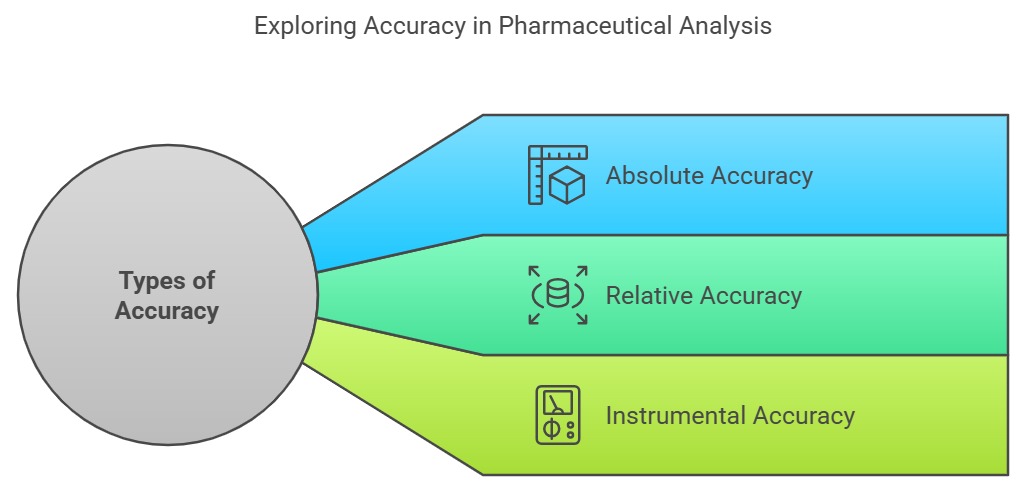
Types of Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
1. Absolute Accuracy
- The direct comparison of a measured value with the actual true value.
- Example: Weighing 10 mg of a drug substance and ensuring the balance reading is precisely 10 mg.
2. Relative Accuracy
- Comparison of the measured value with a reference standard rather than the absolute value.
- Example: Determining the concentration of paracetamol in a tablet by comparing it with a certified reference material (CRM).
3. Instrumental Accuracy
- Accuracy of analytical instruments used in testing, such as HPLC, UV-Vis spectrophotometers, and titrators.
- Example: Ensuring that an HPLC detector provides accurate retention time and peak area values for a drug compound.
Examples of Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
1. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
- Used to quantify APIs in formulations.
- Example: Analyzing the accuracy of an HPLC method for detecting aspirin by spiking known concentrations and calculating the percentage recovery.
2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometry
- Determines drug concentration based on absorbance at a specific wavelength.
- Example: Measuring the absorbance of a standard ibuprofen solution to verify the accuracy of a UV-Vis assay.
3. Titration Methods
- Used for acid-base or redox analysis.
- Example: Potentiometric titration to accurately determine the concentration of hydrochloric acid in a drug formulation.
4. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
- Provides highly accurate identification and quantification of pharmaceutical compounds.
- Example: detecting impurities in a drug sample with a high degree of accuracy using LC-MS.
Factors Affecting Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Analytical Methodology: Poorly designed methods can lead to inaccurate results.
- Instrument Calibration: Regular calibration ensures reliable measurements.
- Human Errors: Sample handling, pipetting, and data recording must be precise.
- Interference from Excipients: Other formulation components can affect accuracy.
- Environmental Conditions: Temperature, humidity, and light exposure can impact results.
How to Improve Accuracy in Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Method Validation: Follow ICH Q2(R1) guidelines to validate accuracy.
- Use Certified Reference Materials: Ensure standard materials are traceable.
- Regular Calibration and Maintenance: Instruments should be routinely calibrated.
- Training and Quality Control: Personnel should be trained to follow SOPs.
- Conduct Recovery Studies: Analyze spiked samples to verify accuracy.
Conclusion
Accuracy is a critical component of pharmaceutical analysis, ensuring that analytical methods provide reliable and reproducible results. By following stringent validation protocols, using high-quality instruments, and minimizing errors, pharmaceutical scientists can achieve high accuracy in drug analysis. This, in turn, contributes to regulatory compliance, patient safety, and the overall quality of pharmaceutical products.
By implementing robust accuracy measures, the pharmaceutical industry can maintain high standards and build trust in the safety and efficacy of medications.




