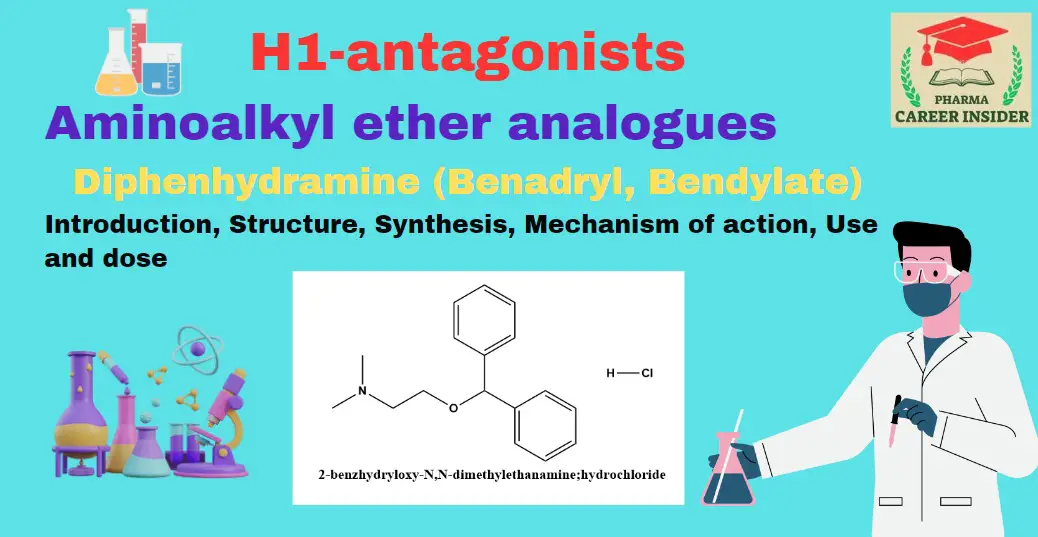
Aminoalkyl ether analogs refer to chemical compounds that share a structural similarity with aminoalkyl ethers. These analogs typically involve the substitution of certain functional groups or moieties while maintaining the basic aminoalkyl ether framework.
The term “aminoalkyl ether” indicates the presence of an amino group (-NH2) and an ether group (-O-) in the molecular structure. Analog development involves modifying specific regions of the molecule to influence properties such as biological activity, stability, or pharmacokinetics.
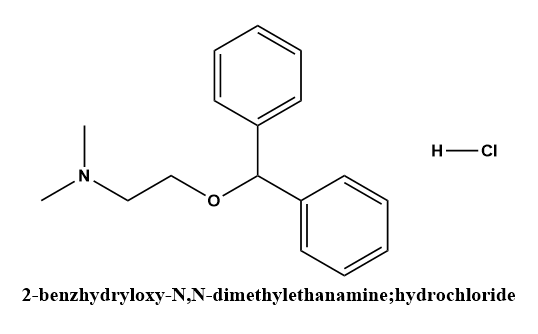
i. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl, Bendylate)
Machenism of action:
Diphenhydramine acts by blocking H1 receptors, reducing histamine-mediated allergic symptoms. Its sedative effect results from crossing the blood-brain barrier, and it possesses antiemetic and antimuscarinic properties.
Properties and uses:
Diphenhydramine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder soluble in water and alcohol. In addition, to antihistaminic activity, diphenhydramine exhibits antiemetic, antitussive, and sedative properties.
Assay:
Dissolve the sample in alcohol, add 0.01 M hydrochloric acids, and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Determine the end-point potentiometrically.
Dose:
The usual dose is 25–50 mg for adults, taken orally three to four times per day with a maximum of 400 mg daily; for skin: use topically 2% of the cream three or four times daily.
Dosage forms:
Diphenhydramine oral solution B.P.