Meta Description
Learn about Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl): its preparation, chemical properties, medicinal uses, and assay methods. Explore its role in cough syrups, kidney treatments, and more!
Introduction
Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) is an inorganic compound widely used in medicine, industry, and laboratory applications. It is commonly known as sal ammoniac and plays a crucial role in pharmaceutical formulations, electrolyte balance, and industrial processes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of general preparation methods, assay techniques, chemical properties, and medicinal uses of ammonium chloride.
General Methods of Preparation of Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride is prepared using various chemical methods. The most common industrial and laboratory preparation methods include:
1. Neutralization Method: Ammonium chloride is synthesized by the reaction of ammonia (NH3) with hydrochloric acid (HCl):
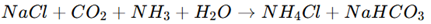
This reaction occurs in an aqueous solution and results in the formation of white crystalline ammonium chloride.
2. Solvay Process (Byproduct Formation): In the Solvay process, ammonium chloride is obtained as a byproduct when sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) is produced from sodium chloride (NaCl), ammonia (NH3), and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Reaction involved:
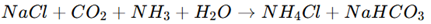
3. Double Decomposition Reaction: Ammonium chloride is obtained by mixing ammonium sulfate and sodium chloride (NaCl), leading to a precipitation reaction.
Assay of Ammonium Chloride
The assay of ammonium chloride is performed to determine its purity and quality. The two primary methods include:
1. Titrimetric Method (Acid-Base Titration)
Principle:
Ammonium chloride is strongly acidic in aqueous solution due to ammonium ion hydrolysis.It is titrated with a standard sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution in the presence of phenolphthalein indicator.
Reaction:
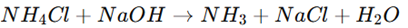
End Point: The solution turns pink when neutralized.
2. Gravimetric Analysis
Principle
Ammonium chloride is converted to ammonia gas (NH3) upon heating.
Procedure:
- 1. Weigh a sample of ammonium chloride.
- 2. Heat the sample and measure the weight loss corresponding to the volatilized ammonia gas.
- 3. The purity is calculated from the weight difference.
Properties of Ammonium Chloride
Physical Properties:
Molecular Formula: NH4Cl
Molecular Weight: 53.49 g/mol
Appearance: White crystalline powder
Solubility: Highly soluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol
Melting Point: Sublimes at 340°C without melting
Chemical Properties:
Thermal Decomposition: Ammonium chloride undergoes sublimation at high temperatures, decomposing into ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl).
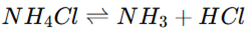
pH Effect: In an aqueous solution, ammonium chloride acts as a weak acid, slightly lowering the pH.
Medicinal Uses of Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride has several therapeutic applications in modern medicine, including:
1. Expectorant in Cough Syrups: Ammonium chloride is used as an expectorant to thin mucus in the respiratory tract, making it easier to expel. It is commonly found in cough syrups and bronchodilator formulations.
2. Acidifying Agent in Urinary Tract Disorders: It helps in the treatment of metabolic alkalosis by acidifying urine, which can prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs).
3. Diuretic for Edema Treatment: Used in diuretic formulations to enhance fluid excretion and treat fluid retention disorders.
4. Electrolyte Replenisher: Ammonium chloride is used in IV fluids to restore electrolyte balance in patients with electrolyte deficiencies.
5. Treatment of Kidney Stones: This helps in the acidification of urine, which can dissolve certain types of kidney stones and prevent new ones from forming.
Conclusion
Ammonium chloride is a versatile compound with numerous medicinal and industrial applications. It plays an essential role in pharmaceuticals, particularly in cough formulations, diuretics, and electrolyte replenishment. Understanding its preparation methods, assay techniques, properties, and medicinal benefits is crucial for its effective utilization.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ammonium chloride used for in medicine?
Answer: Ammonium chloride is used as an expectorant, urinary acidifier, diuretic, and electrolyte replenisher.
2. Is ammonium chloride safe for consumption?
Answer: Yes, when used in prescribed doses. Overconsumption can lead to metabolic acidosis and toxicity.
3. How does ammonium chloride act as an expectorant?
Answer: It thins mucus secretions in the respiratory tract, making it easier to cough out mucus.
4. Can ammonium chloride be used for kidney health?
Answer: Yes, it helps acidify urine, which can aid in kidney stone treatment and prevent UTIs.
5. What happens if ammonium chloride is heated?
Answer: It sublimates into ammonia (NH3) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) when exposed to heat.




