Introduction
Astemizole, once a notable antihistamine in the treatment of allergies, has a history marked by its withdrawal from the market due to safety concerns. Prescribers traditionally recommended it for allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria, as it is an antagonist at H1 histamine receptors. However, its withdrawal stemmed from the recognition of potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias associated with its use.
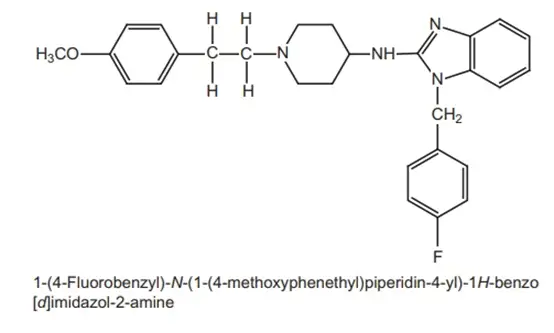
Structure
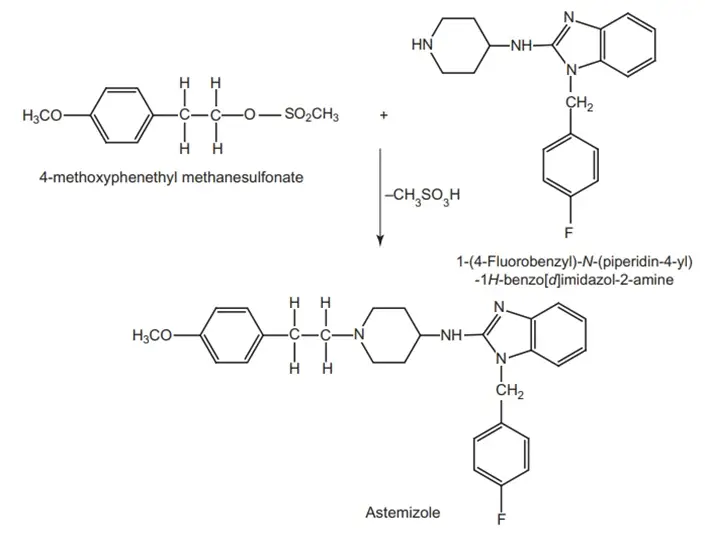
Synthesis
Mechanism of action
Astemizole selectively antagonizes the H1 histamine receptors, inhibiting the action of histamine by binding to these receptors. This inhibition prevents the biological effects mediated by histamine in various tissues.
Properties and uses:
Astemizole is a white powder, practically insoluble in water and soluble in methylene chloride, methanol, and alcohol. It is used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic urticaria. It is an effective antiallergic agent against asthma, hay fever, and chronic urticaria.
Assay:
Dissolve the sample in a mixture of anhydrous acetic acid and methyl ethyl ketone and titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid using naphtholbenzein solution as an indicator.
Dose:
The usual dose is 10 mg (oral), increased, if required, to 30 mg daily for up to 7 days one h before meals.



