What Are Biphasic Liquids?
Biphasic liquids are specialized liquid dosage forms that consist of two immiscible phases, typically an aqueous phase and an oil or solid phase. These formulations require shaking before use to ensure uniform distribution of the active ingredients. Widely used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food industries, biphasic liquids provide stability for drugs and enhance bioavailability.
Their unique structure allows them to function as suspensions or emulsions, depending on whether they contain solid particles or liquid-liquid dispersions. Due to their diverse applications, they play a critical role in drug formulations, skincare products, and even food processing.
“A biphasic liquid is a heterogeneous liquid formulation containing two separate phases that do not mix permanently. These phases require agitation before administration to ensure homogeneity.“
Key Features of Biphasic Liquids:
- Two separate liquid or solid-liquid phases
- Requires shaking before use
- Used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food
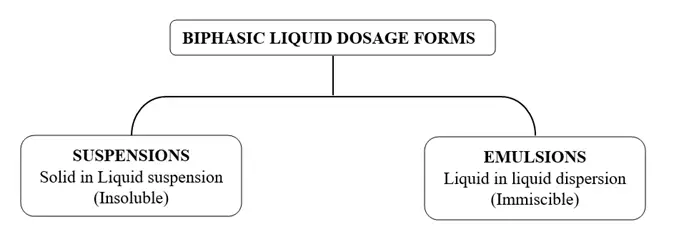
Types of Biphasic Liquids
Biphasic liquids are classified into two main types:
- Suspensions: Solid particles dispersed in a liquid medium (e.g., antacid suspensions, antibiotic suspensions).
- Emulsions: A liquid-liquid dispersion where one liquid is dispersed in another immiscible liquid (e.g., oil-in-water and water-in-oil emulsions).
How Are Biphasic Liquids Prepared?
Ingredients Required:
- Active pharmaceutical ingredients (API): Medicinal agents (e.g., antibiotics, vitamins).
- Suspending agents: Improve stability (e.g., gelatin, methylcellulose).
- Emulsifiers: Help mix immiscible liquids (e.g., lecithin, polysorbates).
- Preservatives: Prevent microbial growth (e.g., sodium benzoate, parabens).
- Flavors and Sweeteners: Improve taste (e.g., sucrose, sorbitol).
- Viscosity Enhancers: Ensure uniform distribution (e.g., xanthan gum, agar).
Steps in Preparation:
- Dissolve the active ingredient in the appropriate phase (aqueous or oil).
- Add suspending or emulsifying agents to maintain uniformity.
- Mix the two phases thoroughly under controlled conditions.
- Homogenize or sonicate the mixture to ensure proper dispersion.
- Add preservatives, flavors, or stabilizers as required.
- Store in a well-labeled, airtight container with instructions for shaking before use.
Common Uses of Biphasic Liquids in Different Industries
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Used for drugs that are unstable in a single phase (e.g., pediatric suspensions, emulsified pain relievers).
- Cosmetic Industry: Found in skincare products like cleansing emulsions and sunscreen lotions.
- Food Industry: Used in salad dressings and flavored emulsions.
- Chemical Industry: Applied in pesticides, paints, and industrial formulations.
Key Benefits of Biphasic Liquid Formulations
- Improved Stability: Reduces degradation of sensitive drugs.
- Better Drug Absorption: Enhances bioavailability of certain compounds.
- Versatile Applications: Used across multiple industries.
- Enhanced Taste and Appearance: Especially in pharmaceutical syrups and suspensions.
- Customizable Formulations: They can be tailored to specific needs with emulsifiers and stabilizers.
Precautions and Storage
- Shake Well Before Use: This ensures uniformity before administration.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: This prevents phase separation and degradation.
- Use Within Expiry Date: This ensures effectiveness and safety.
- Check for Sedimentation: Some suspensions require re-dispersion before consumption.
- Follow Prescribed Dosage: To avoid underdosing or overdosing.
Conclusion
Biphasic liquids play a vital role in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food processing, offering versatile and stable formulations for various applications. Their ability to suspend solid or liquid components makes them essential in modern formulations. Proper preparation, storage, and usage ensure their effectiveness and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are biphasic liquids?
Answer: Biphasic liquids are two-phase liquid systems, such as suspensions and emulsions, that require shaking before use.
2. What is the difference between suspensions and emulsions?
Answer: Suspensions contain solid particles in a liquid, while emulsions consist of one liquid dispersed in another immiscible liquid.
3. Why do biphasic liquids need shaking before use?
Answer: Since the two phases do not mix permanently, shaking ensures even distribution of the active ingredient before administration.
4. What are some examples of biphasic liquid formulations?
Answer: Examples include antacid suspensions, pediatric antibiotic suspensions, and emulsified pain relievers.
5. How should biphasic liquids be stored?
Answer: To maintain effectiveness, they should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and shaken before use.

