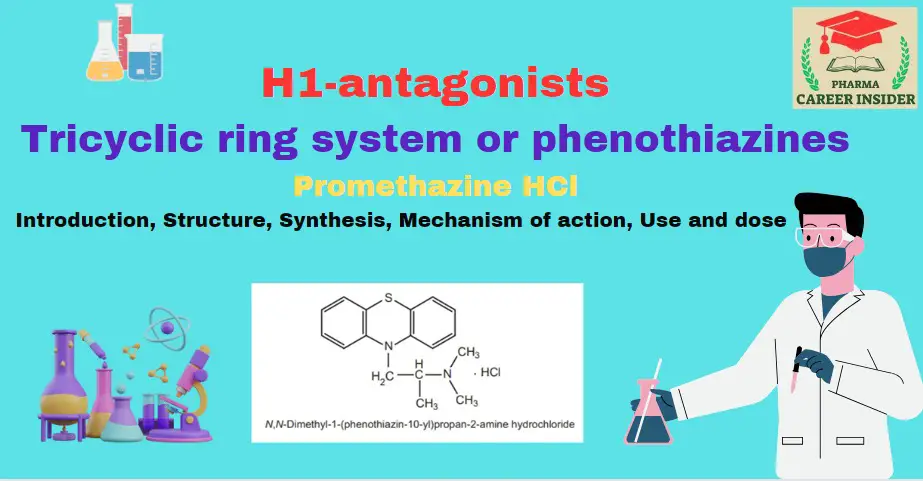
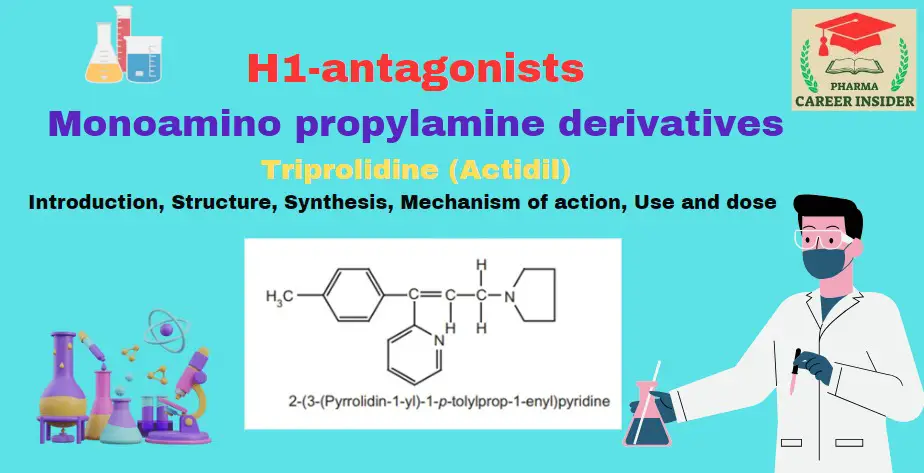
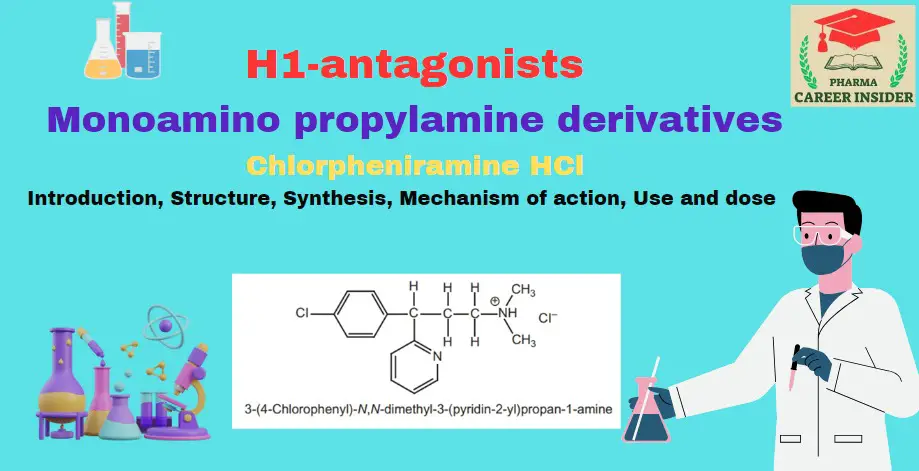
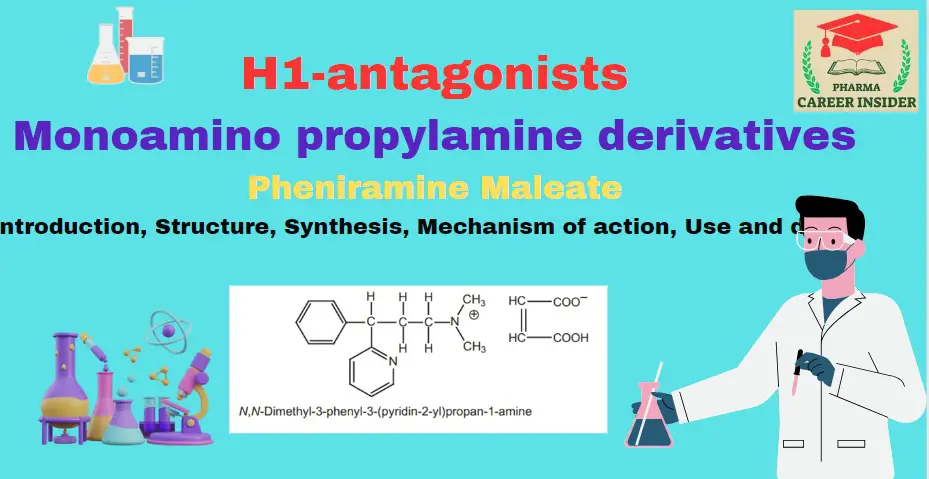
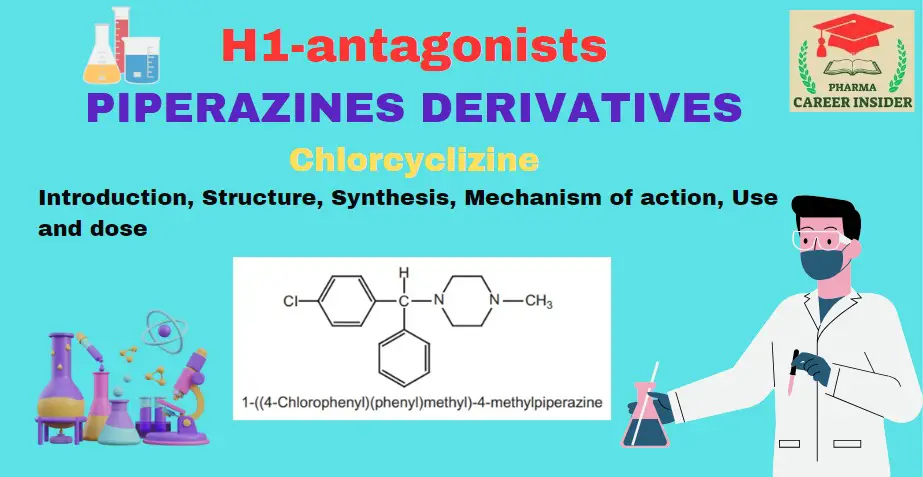
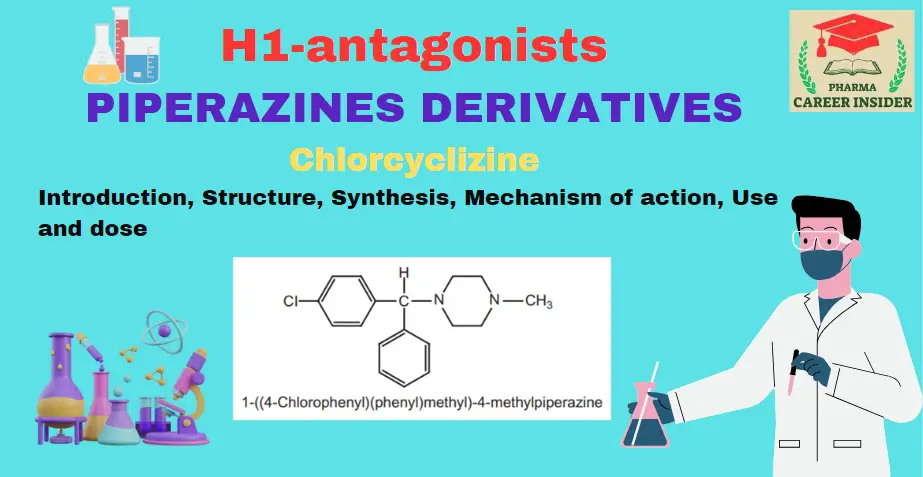
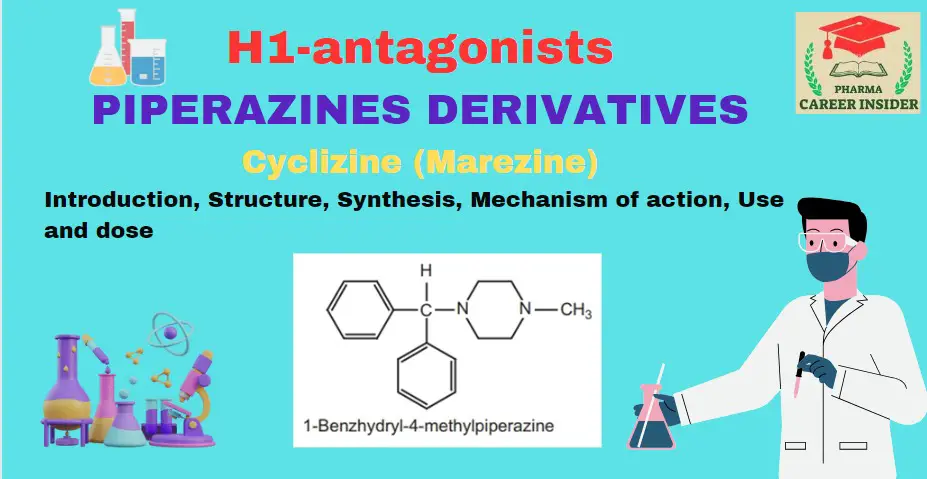
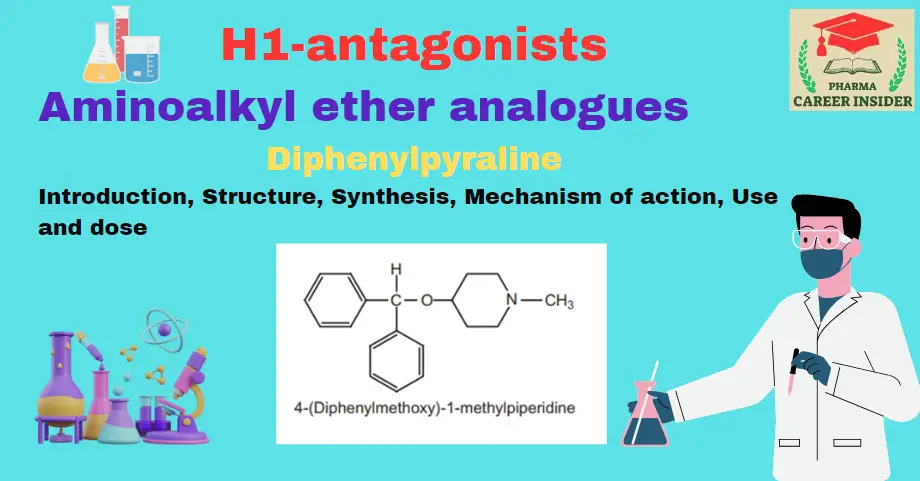
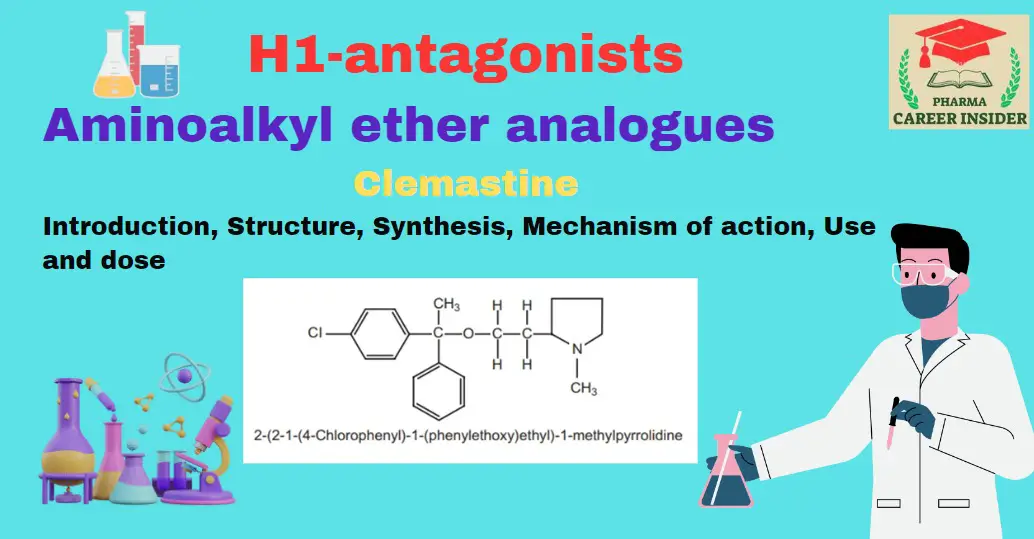
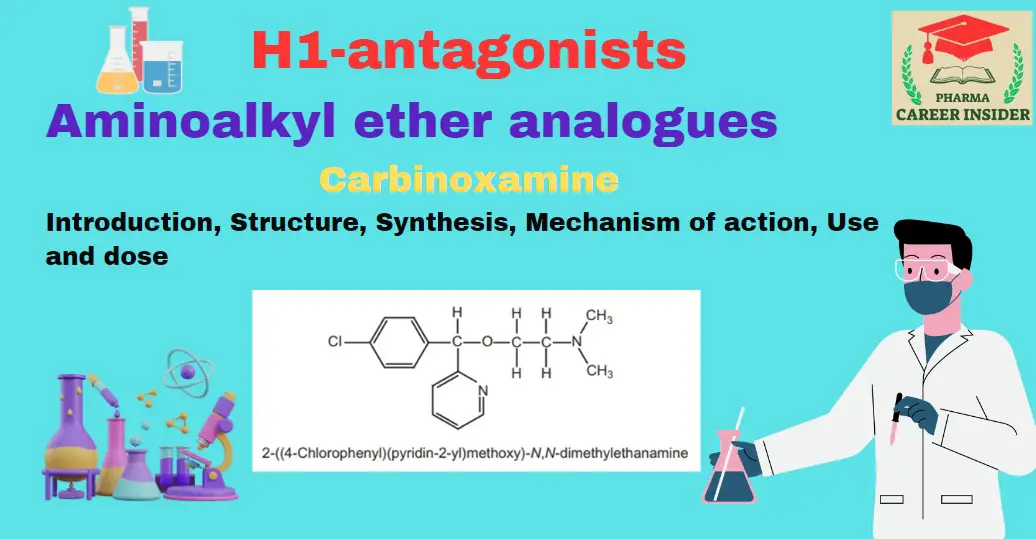
Tricyclic ring system or phenothiazines
1. Promethazine HCl (Phenargen) Promethazine HCl is a versatile medication within the phenothiazine class, acclaimed for its multifaceted pharmacological properties. As an antagonist at H1 histamine receptors, it effectively mitigates allergic symptoms, while its antimuscarinic actions contribute to potent antiemetic effects. Widely utilized to alleviate symptoms ranging from allergic reactions to motion sickness and nausea, promethazine … Read more