Anthracene, a chemical compound, participates in addition and electrophilic substitution reactions, with a preference for occurring at the C-9 and C-10 positions. This preference can be rationalized by examining the intermediate carbonium ions generated from attacks at C-1, C-2, and C-9 (where other positions are symmetrical equivalents of 1, 2, or 9). In the equations provided below, “E+” represents an electrophile.
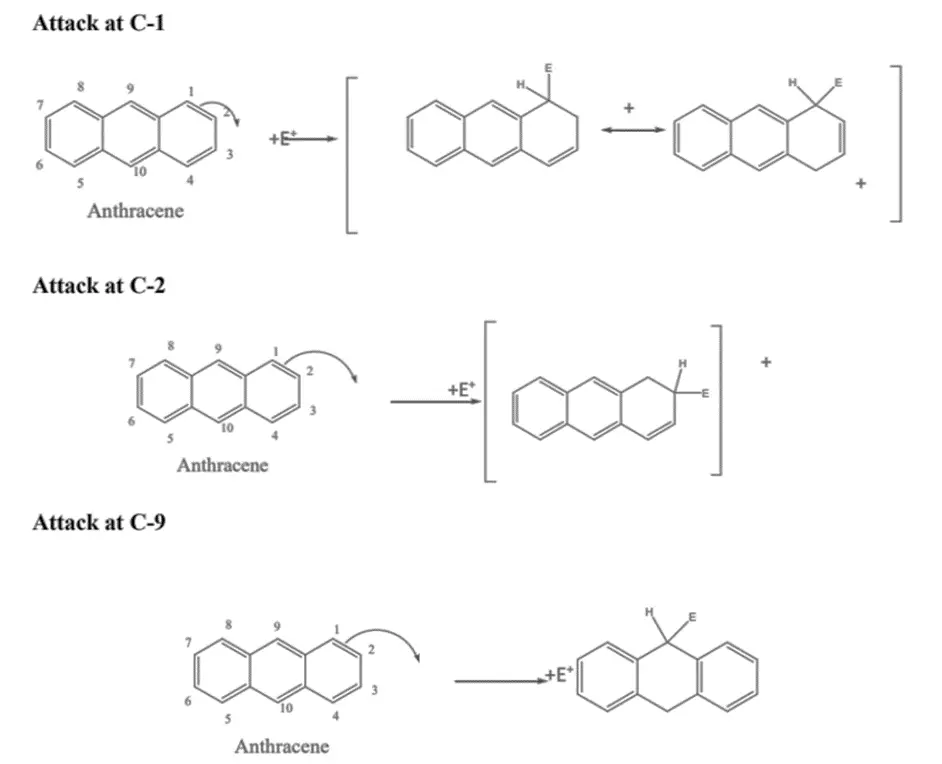
Attacking at C-9 results in the formation of an intermediate carbonium ion where two benzene rings are preserved. Conversely, attacking at C-1 or C-2 leads to an intermediate where a naphthalene system is conserved. The formation of the former intermediate is favored due to its higher stability, attributed to the resonance energy of two benzene rings (2 * 36 = 72 kcal), which exceeds that of naphthalene (61 kcal).
Chemical reactions
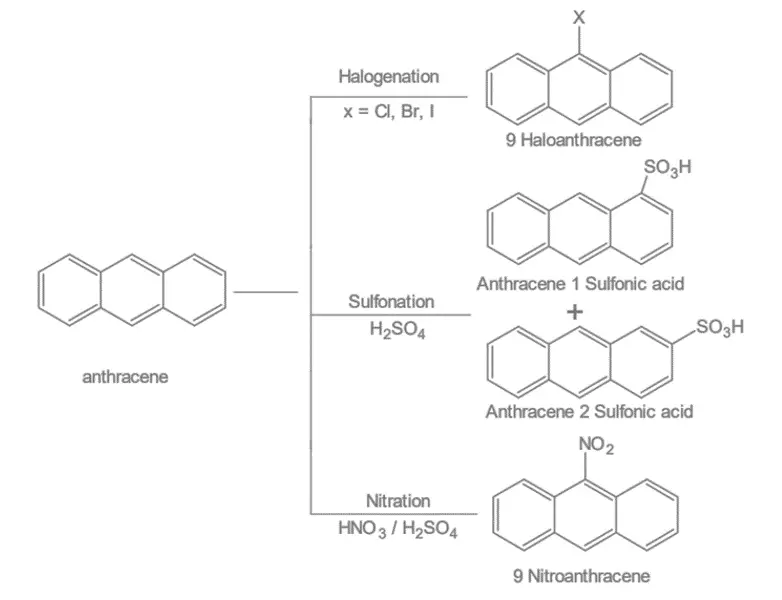
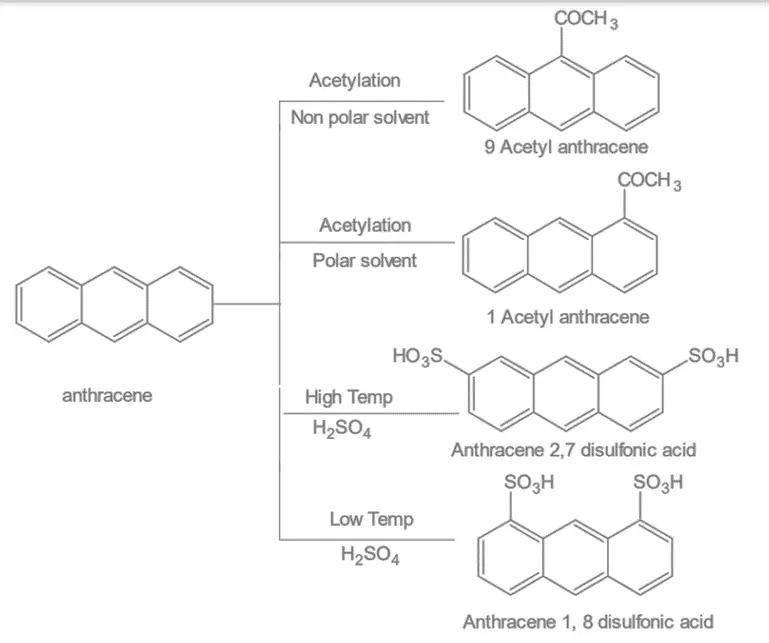
1. Electrophilic substitution reaction: Anthracene undergoes different electrophilic substitution reactions like halogenation, sulphonation, nitration etc.
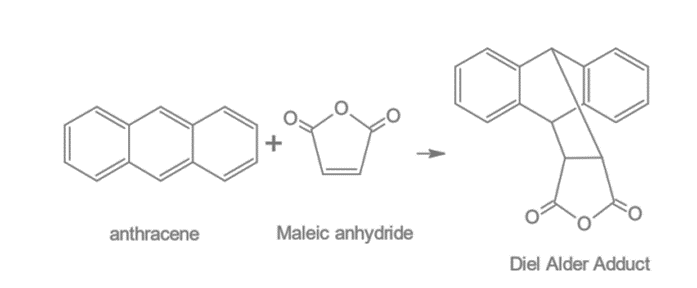
2. Diels-Alder Reaction: Anthracene undergoes Diels-Alder reaction at 9, 10 positions and forms endo anthracene maleic anhydride.
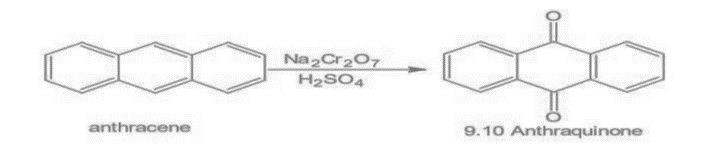
3. Oxidation: Anthracene oxidizes with sodium dichromate and sulfuric acid to form 9, 10 anthraquinone.
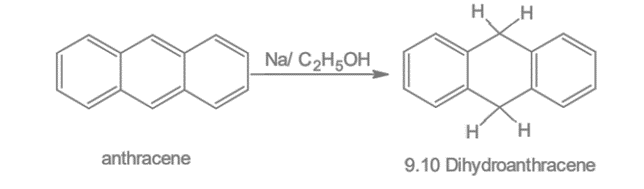
4. Reduction: Anthracene on reduction with sodium and ethyl alcohol produces 9, 10 dihydroanthracene.
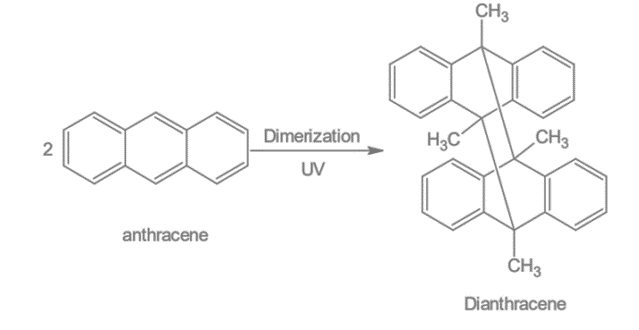
5. Dimerisation: Dimerization of anthracene in UV light produces Di anthracene.
Discover the chemical properties of anthracene, a compound known for its involvement in addition and electrophilic substitution reactions, particularly favoring positions C-9 and C-10. Examining intermediate carbonium ions makes this preference evident, with attacks at C-9 preserving two benzene rings favored for their stability. Anthracene participates in various reactions, including electrophilic substitution, Diels-Alder reaction, oxidation to form anthraquinone, reduction to produce dihydroanthracene, and dimerization yielding Di anthracene under UV light. Explore the versatile chemical reactivity of anthracene.



