Meta Description:
Discover the chemical properties of aromatic amines, including their reactivity, key reactions, and applications in pharmaceuticals and organic synthesis.
Introduction
Aromatic amines, which contain amino (-NH2) groups attached to a benzene ring, exhibit various chemical properties. Here are some key chemical properties of aromatic amines:
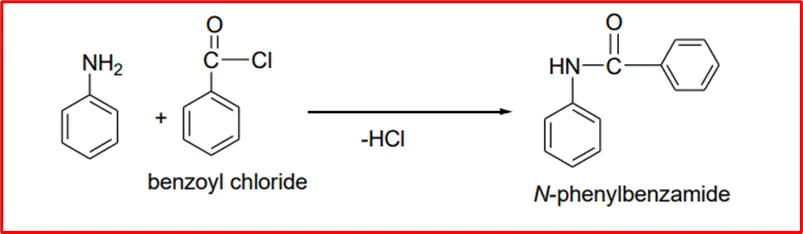
1. Formation of amides: When aromatic amines react with acyl chloride, they produce benzylamide with the formation of amide linkage.
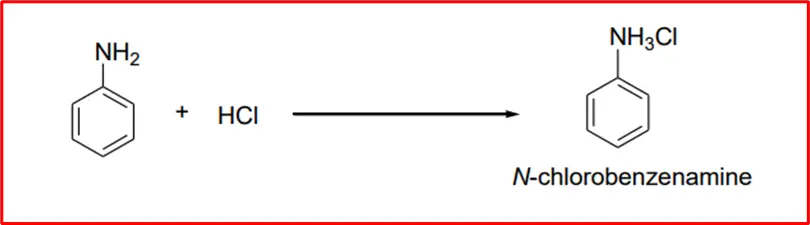
2. Formation of salt: When an aromatic amine is treated with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it results in the formation of benzeneaminium chloride.
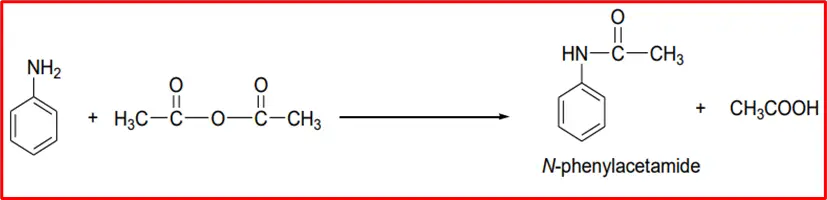
3. Acetylation: When an aromatic amine is treated with acetic anhydride, it reacts to form acetanilide.
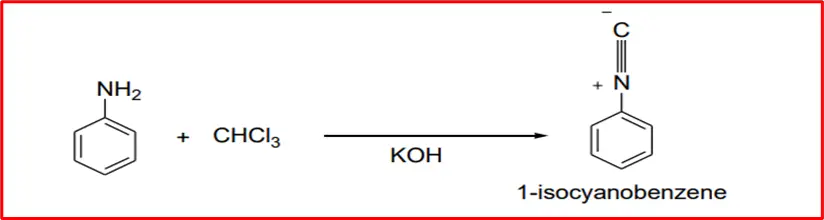
4. Carbylamine Reaction: When aniline reacts with chloroform and potassium hydroxide, it produces carbylamine.
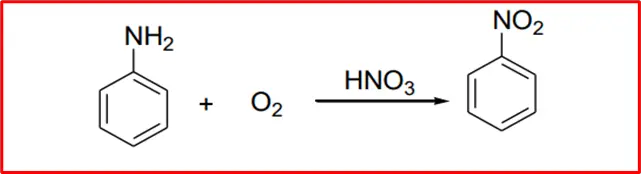
5. Oxidation: When aromatic amines are oxidized in the presence of nitric acid, nitrobenzene is produced.
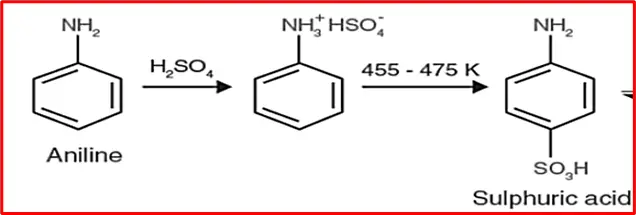
6. Sulphonation: Sulfuric acid reacts with aniline to form anilinium hydrogen sulfate. Upon heating, it produces sulphanilic acid.
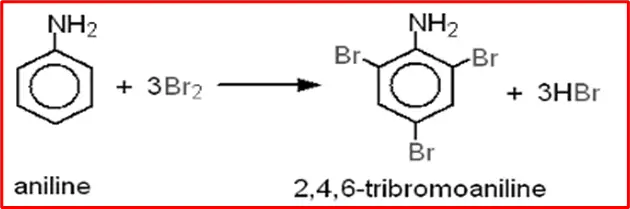
7. Halogenation: When aniline comes into contact with halogens such as bromine and chlorine, it undergoes a reaction that results in the formation of 2,4,6-tribromoaniline.
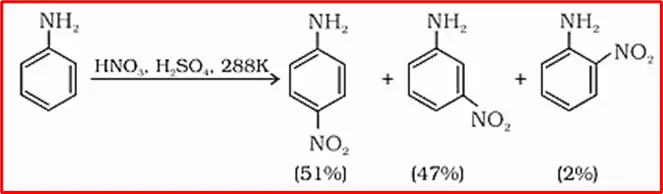
8. Nitration: Nitration of aniline in a strongly acidic medium yields a mixture of o-nitroaniline, p-nitroaniline, and m-nitroaniline. Aniline’s -NH2 group, which has an ortho, para-directing effect, is present on the benzene ring.
Conclusion
Aromatic amines exhibit unique chemical properties due to the interaction between the amino group and the aromatic ring. Their reactivity is influenced by electron-donating and withdrawing effects, leading to various important reactions such as acetylation, oxidation, and electrophilic substitution. These compounds play a crucial role in the synthesis of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and polymers. Understanding their chemical behavior helps in optimizing their applications in different industries while ensuring safe handling due to their potential toxicity.




