Cycloalkanes are a class of hydrocarbons with a circular arrangement of carbon atoms. Due to the cyclic structure, these compounds possess a certain degree of strain, which affects their chemical properties. While cycloalkanes display lower reactivity than their open-chain counterparts, they can still partake in various chemical reactions.
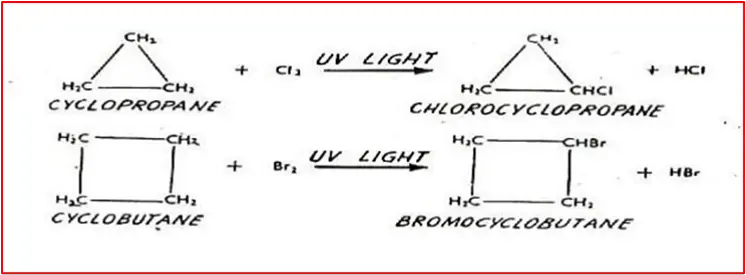
1. Halogenation in the presence of UV light: Produce mono-substituted halogen without breaking the ring.
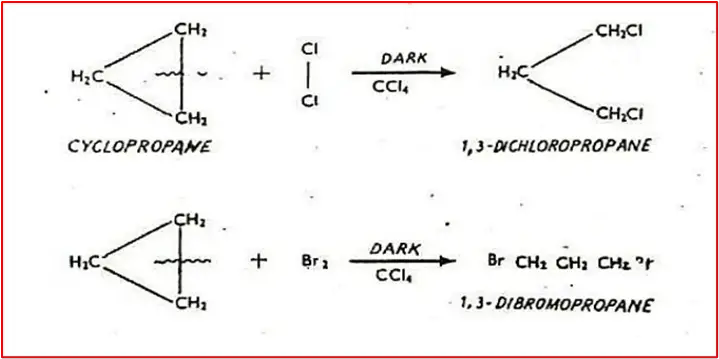
2. Addition of Cl2/Br2 in the presence of CCl4 in the dark: At room temperature and without diffused sunlight, cyclopropane reacts with Cl2/Br2 to produce 1,3-dichlorocyclopropane and 1,3-dibromo cyclopropane, respectively. This reaction breaks one of the carbon-carbon bonds in cyclopropane and causes the two halogen atoms to appear at the ends of the propane chain.
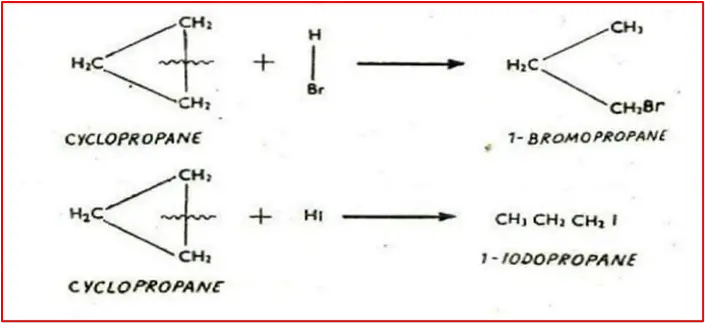
3. Reaction with concentrated HBr and HI: Produce 1-bromopropane and 1-iodopropane, respectively, with ring braking.
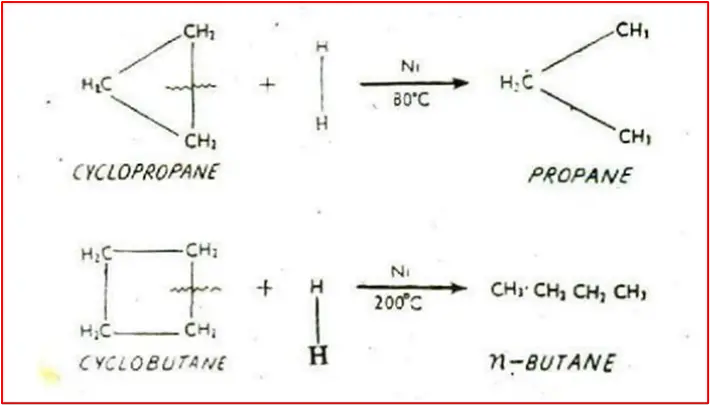
4. Addition of Hydrogen / Catalytic Reduction: Cyclopropane and Cyclobutane react with hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst to produce n-propane and n-butane, respectively. Cyclopentane and higher members of the family do not undergo this reaction.