Introduction
Chlorcyclizine is a piperazine-class antihistamine with antiemetic properties commonly utilized to prevent and relieve nausea and vomiting, particularly in the context of motion sickness. With its mechanism of action as an H1 receptor antagonist, it not only mitigates the effects of histamine but also exhibits antimuscarinic properties, contributing to its effectiveness in managing motion-induced symptoms. Often administered orally in tablets or syrup, chlorcyclizine is recognized for relieving allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis.
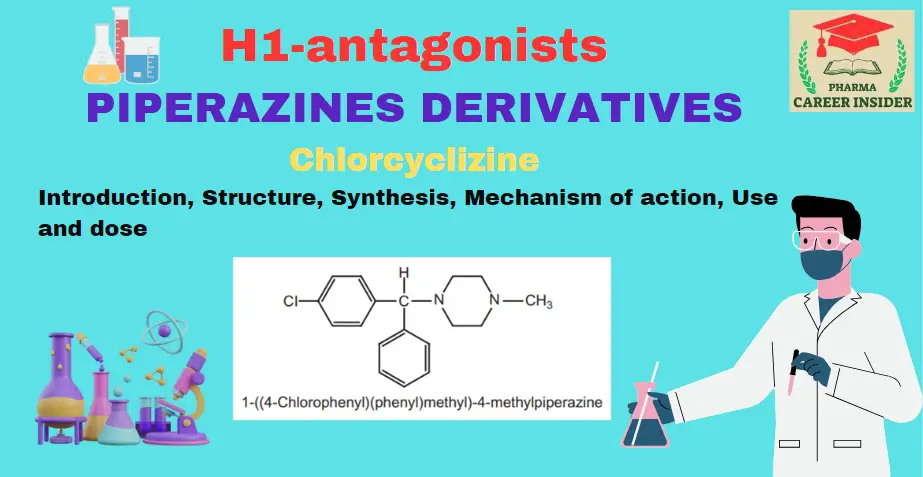
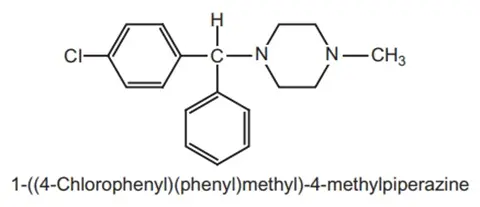
Structure
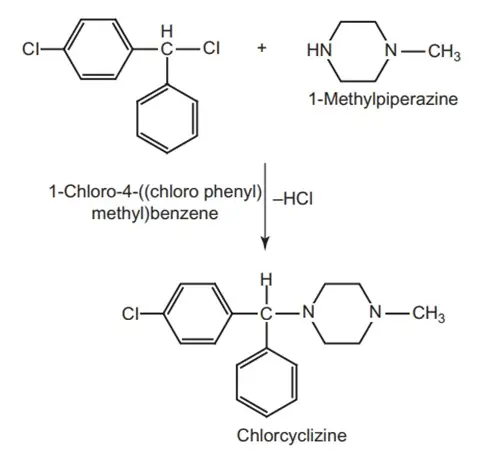
Synthesis
Mechanism of action
- H1 Receptor Antagonism:
- Chlorcyclizine blocks the effects of histamine on H1 receptors.
- By inhibiting histamine action, it mitigates allergic reactions and motion sickness symptoms.
- Antimuscarinic Properties:
- Chlorcyclizine exhibits antimuscarinic or anticholinergic effects.
- This contributes to its antiemetic (anti-nausea) properties by affecting the activity of acetylcholine in the central nervous system.
Properties and uses
Chlorcyclizine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder, soluble in water, methylene chloride, and alcohol. Substitution of halogen in the 2nd or 3rd position of either of the benzhydryl rings results in a much less potent activity. Chlorcyclizine is indicated in the symptomatic relief of urticaria, hay fever, and other allergic conditions.
Dose
The usual dose is 50–200 mg per day.