Introduction
An electrochemical cell is a device that generates electrical energy from chemical reactions or uses electrical energy to drive chemical reactions. These cells are fundamental in electrochemistry and have various applications in energy storage, corrosion studies, electroplating, and industrial processes.
Electrochemical cells operate based on redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions, where electrons are transferred between chemical species. Depending on their function, electrochemical cells are classified into galvanic (voltaic) cells and electrolytic cells.
Types of Electrochemical Cells
1. Galvanic (Voltaic) Cell
A galvanic cell is an electrochemical cell that converts chemical energy into electrical energy through spontaneous redox reactions. These cells are commonly used in batteries.
Components of a Galvanic Cell
- Two Electrodes:
Anode (-): Site of oxidation (loss of electrons).
Cathode (+): Site of reduction (gain of electrons).
- Electrolytes: Ionic solutions that conduct electricity.
- Salt Bridge: Maintains electrical neutrality by allowing the movement of ions.
- External Circuit: Allows electron flow from the anode to the cathode.
1. Daniel Cell (Zn-Cu Cell)
A Daniel cell is a classic galvanic cell consisting of:
- Anode: Zinc (ZnZn) electrode in ZnSO4ZnSO_4 solution.
- Cathode: Copper (CuCu) electrode in CuSO4CuSO_4 solution.
- Salt Bridge: Contains an inert electrolyte (e.g., KCl) to balance charge.
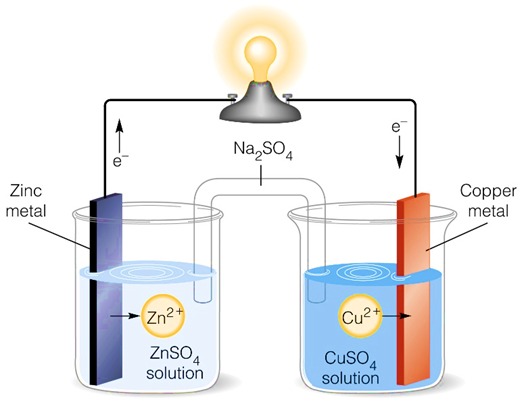
Reactions in Daniel Cell:

The positive cell potential indicates a spontaneous reaction, meaning the galvanic cell produces electricity.
2. Electrolytic Cell
An electrolytic cell is an electrochemical cell that uses electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. This process is called electrolysis and is widely used in industry.
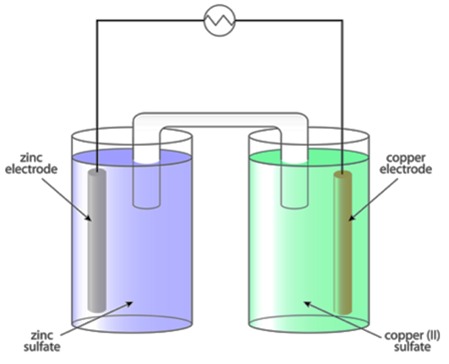
Components of an Electrolytic Cell
- Two Electrodes:
Anode (+): Oxidation occurs here.
Cathode (-): Reduction occurs here.
- Electrolyte: The ionic solution that facilitates electron movement.
- Power Source: Provides external electrical energy to drive the reaction.
Example: Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis of water (H2O) produces hydrogen and oxygen gases.
Reactions:

Since the reaction is non-spontaneous, a power source (battery) is required.
Applications of Electrolytic Cells
- Electroplating (coating metals like gold, silver, or nickel).
- Electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen fuel.
- Industrial extraction of metals (e.g., aluminum from bauxite via the Hall-Heroult process).
- Purification of metals like copper.
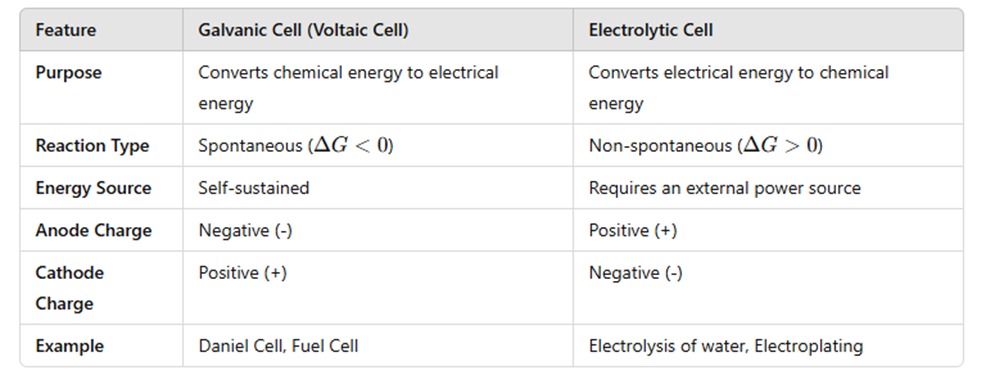
Difference Between Galvanic and Electrolytic Cells
Nernst Equation and Cell Potential
The Nernst equation is used to determine the electrode potential at any given concentration:

The Nernst equation is particularly useful for understanding how concentration changes affect the potential of an electrochemical cell.
Applications of Electrochemical Cells
1. Batteries and Energy Storage
- Primary Batteries (Non-rechargeable): dry cell, alkaline battery.
- Secondary Batteries (Rechargeable): lead-acid battery, lithium-ion battery.
- Fuel cells: Convert hydrogen or methanol into electricity.
2. Industrial Applications
- Electrolysis for Metal Extraction: Extraction of aluminum, sodium, and chlorine.
- Electroplating: Coating metals with a thin layer of another metal (e.g., gold plating).
- Corrosion Prevention: Cathodic Protection Techniques.
3. Environmental Applications
- Water Purification: Removal of heavy metals via electrochemical processes.
- Electrochemical Sensors: Used in pollution monitoring (e.g., pH meters, gas sensors).
4. Biomedical and Healthcare Applications
- Pacemakers and implantable batteries.
- Glucose Sensors for Diabetes Monitoring.
Conclusion
Electrochemical cells play a crucial role in modern science and technology. Galvanic cells provide a sustainable way to generate electricity, while electrolytic cells drive industrial and chemical processes. Understanding their working principles, applications, and differences is essential in fields like energy storage, material science, and environmental protection.




