Emulsions are essential in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and the food industry, helping to deliver active ingredients effectively. These biphasic liquid systems consist of two immiscible liquids (oil and water) stabilized by emulsifying agents. Emulsions play a crucial role in drug formulations, enhancing bioavailability, stability, and controlled drug release.
In this article, we explore the definition, types, preparation methods, advantages, disadvantages, and real-world applications of emulsions.
What Are Emulsions?
An emulsion is a heterogeneous system in which one immiscible liquid is dispersed in another with the help of emulsifying agents to form a stable mixture. These systems are widely used in medical, cosmetic, and food formulations for improved solubility and stability.
Key Characteristics of Emulsions:
- Consist of two immiscible liquids (oil and water).
- Require an emulsifier for stability.
- Exhibit thermodynamic instability, requiring proper formulation techniques.
- It can be classified based on droplet size and dispersion phase.
Types of Emulsions and Their Applications
Emulsions are categorized based on the dispersed phase, continuous phase, and droplet size.
1. Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions
- Oil droplets dispersed in a water phase.
- Common in pharmaceutical formulations like creams, lotions, and syrups.
- Example: Milk, vanishing creams.
2. Water-in-Oil (W/O) Emulsions
- Water droplets dispersed in an oil phase.
- Often used in cosmetics (cold creams) and medicated ointments.
- Example: Butter, cod liver oil emulsion.
3. Multiple Emulsions (O/W/O or W/O/W)
- Consist of double emulsions, providing controlled drug release.
- Used in sustained-release pharmaceutical formulations and high-end cosmetics.
- Example: Anti-aging cosmetic formulations.
4. Microemulsions & Nanoemulsions
- Transparent and thermodynamically stable emulsions.
- Used in drug delivery systems, enhancing bioavailability.
- Example: Nano-emulsions in vaccines and pharmaceutical suspensions.
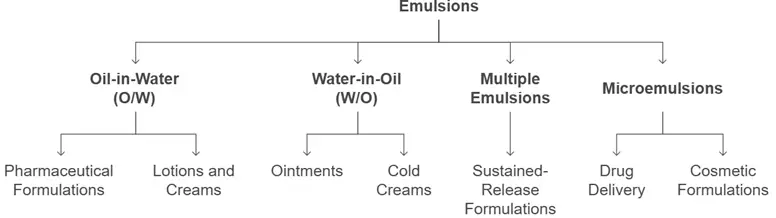
Figure: Types of Emulsions and Their Applications
Emulsion Preparation Methods
Formulating stable emulsions requires appropriate mixing techniques and emulsifying agents. Below are common methods:
1. Mechanical Stirring Method
- Uses high-speed mechanical mixers to disperse one phase into another.
- Common in pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
- Example: Creams and lotions preparation.
2. Homogenization Method
It involves passing the emulsion through a homogenizer at high pressure.
Produces fine, uniform droplets, enhancing stability.
Example: Milk homogenization in dairy industries.
3. Phase Inversion Method
- Converts O/W emulsions to W/O and vice versa.
- Achieved by changing phase volume ratios or temperature.
- Example: Certain pharmaceutical formulations.
4. Ultrasonication Method
- Uses high-frequency ultrasonic waves to break droplets into nano-sizes.
- Produces highly stable nano-emulsions.
- Example: Intravenous drug emulsions.
5. Addition of Emulsifiers
- Uses surfactants like Tween, Span, lecithin, and natural gums.
- Prevents phase separation and enhances stability.
- Example: Soft drink emulsions.
6. Bottle Method (Small-Scale Preparation)
- A simple shaking method is used for extemporaneous emulsions.
- Example: Pharmacy-based liquid emulsions.
Key Benefits of Emulsions in Pharmaceuticals & Cosmetics
Emulsions offer various advantages in the medical, cosmetic, and food industries.
- Enhanced Drug Absorption: Increases bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
- Improved Stability: Protects sensitive drugs from oxidation and degradation.
- Taste Masking: Oil-based drugs taste better in emulsified forms.
- Controlled Drug Release: Supports sustained-release and targeted delivery.
- Versatile Applications: Used in pharmaceuticals, skincare, and food industries.
Challenges & Limitations of Emulsions
Despite their advantages, emulsions pose several challenges:
- Physical Instability: Prone to creaming, flocculation, and phase separation.
- Complex Formulation: Requires precise emulsifier selection.
- Storage Issues: Sensitive to temperature, light, and microbial growth.
- High Energy Requirement: Some methods need specialized equipment.
How to Overcome Stability Issues?
- Use optimized emulsifiers and surfactants.
- Maintain proper pH and temperature conditions.
- Store in airtight, light-resistant containers.
- Use preservatives to prevent microbial growth.
Real-World Applications of Emulsions
1. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Oral and intravenous drug formulations.
- Nanoemulsions in vaccine development.
2. Cosmetic Industry:
- Moisturizers, creams, and sunscreens.
- Anti-aging and skin-lightening formulations.
Food Industry:
- Mayonnaise, salad dressings, and dairy products.
- Flavor emulsions in soft drinks.
Conclusion
Emulsions are a vital part of modern pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food formulations. Their ability to enhance solubility, stability, and bioavailability makes them a preferred choice in various industries. However, stability challenges must be addressed using optimized emulsifiers, proper formulation techniques, and controlled storage conditions.
Would you like to explore more advanced emulsion technologies? Let us know in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are emulsions and their types?
Answer: Emulsions are biphasic liquid systems of oil and water stabilized by an emulsifier. The main types include O/W, W/O, multiple emulsions, and nanoemulsions.
2. How are emulsions prepared?
Answer: Emulsions are prepared using homogenization, ultrasonication, and phase-inversion methods.
3. What is the role of emulsifiers in emulsions?
Answer: Emulsifiers reduce surface tension and prevent phase separation.
4. How can emulsions be stabilized?
Answer: Using surfactants, proper homogenization, and optimal storage conditions.
5. What are the common applications of emulsions?
Answer: They are used in drug formulations, cosmetics, food processing, and vaccine development.