Anthracene can be prepared through several methods, including:
1. By Friedal Craft reaction:
Anthracene can be synthesised via the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction, where benzyl chloride reacts with itself in a Lewis acid catalyst like aluminium chloride. This forms di(phenylethyl)benzene, which can then be cyclized to yield anthracene.
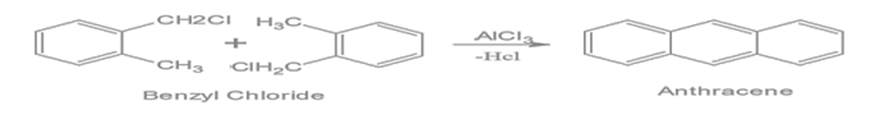
2. By Haworth Synthesis
Step I:
Benzene reacts with phthalic anhydride in the presence of AlCl3 to produce O-Benzoyl benzoic acid.
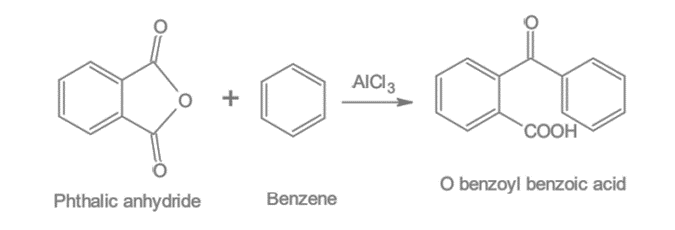
Step II:
When O-benzoyl benzoic acid is heated with concentrated sulfuric acid, it produces 9,10-anthraquinone.
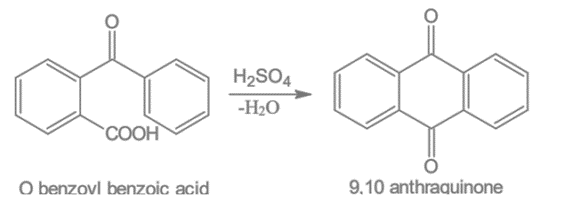
Step III:
When 9,10-anthraquinone is distilled with zinc dust, it results in the production of anthracene.
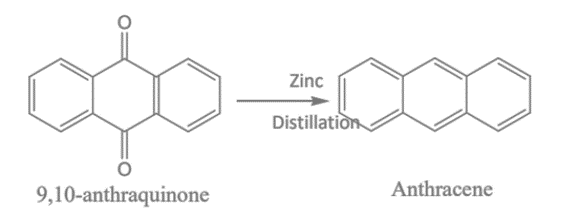
3. By Elbs Reaction:
Elbs reaction refers to the intermolecular condensation of a diaryl ketone with a methyl or methylene substituent ortho to the carbonyl group, forming an aromatic compound.
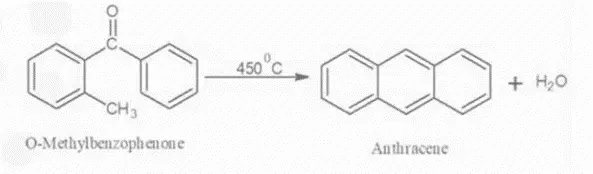
4. By Diels Alder reaction:
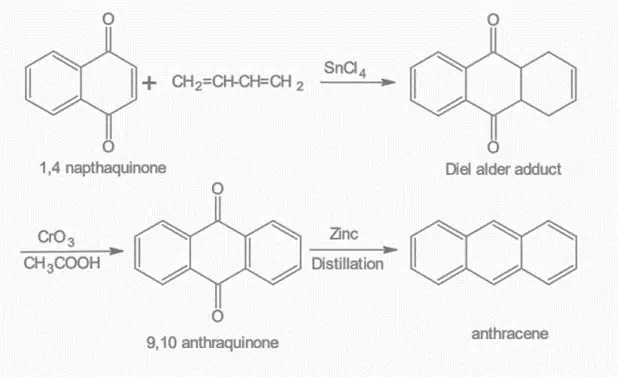
This reaction involves the combination of naphthoquinone and 1,3-butadiene. The resulting product is then oxidized using chromium trioxide in glacial acetic acid, which forms 9,10 anthraquinone. Finally, the anthraquinone is distilled with zinc dust to yield anthracene.
Conclusion:
Prepare anthracene using various methods, including Friedel-Crafts alkylation, Haworth Synthesis, Elbs Reaction, and Diels-Alder reaction. In Friedel-Crafts alkylation, benzyl chloride reacts with itself in the presence of a Lewis acid catalyst to form di(phenylethyl)benzene, which cyclizes to yield anthracene. In Haworth Synthesis, benzene reacts with phthalic anhydride to produce O-Benzoyl benzoic acid, which, upon heating with sulfuric acid, yields 9,10-anthraquinone. Distillation of 9,10-anthraquinone with zinc dust results in anthracene. The Elbs reaction involves intermolecular condensation of a diaryl ketone with a methyl or methylene substituent ortho to the carbonyl group. The Diels Alder reaction combines naphthoquinone and 1,3-butadiene, followed by oxidation and distillation with zinc dust to yield anthracene.



