Monoamino propylamine derivatives” refers to a group of chemical compounds derived from monoamino propylamine. This group includes compounds with a structural basis similar to monoamino propylamine, but they undergo chemical modifications to yield diverse derivatives.
Saturated analogues
Pheniramine Maleate (Avil, Polarmine)
Introduction
Pheniramine maleate is an antihistamine widely recognized for its efficacy in providing relief from symptoms associated with allergic reactions. Functioning as an antagonist at the H1 histamine receptors, it effectively mitigates manifestations like itching, sneezing, and a runny nose. Commonly employed in treating allergic rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis, and skin conditions causing itching, pheniramine maleate is available in various formulations, including tablets and syrups. As with any pharmaceutical agent, its use should align with healthcare professional guidance for optimal safety and effectiveness.
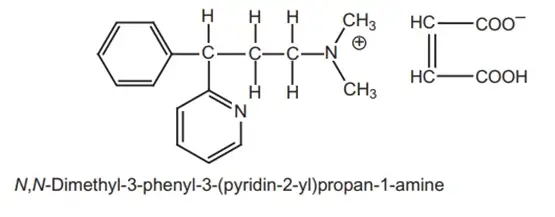
Structure
Synthesis
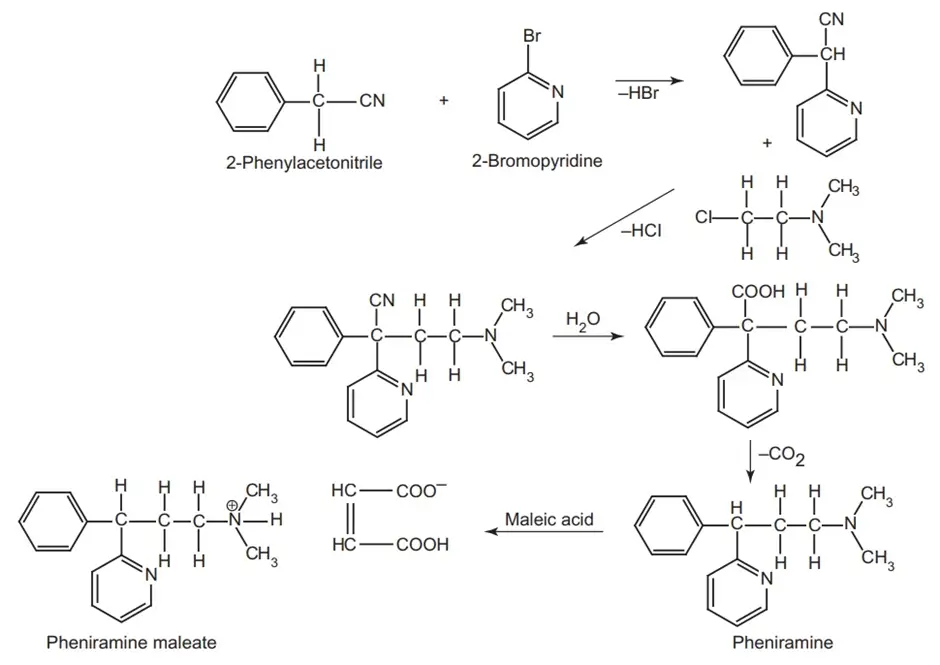
Route I. From 2-Phenylacetonitrile
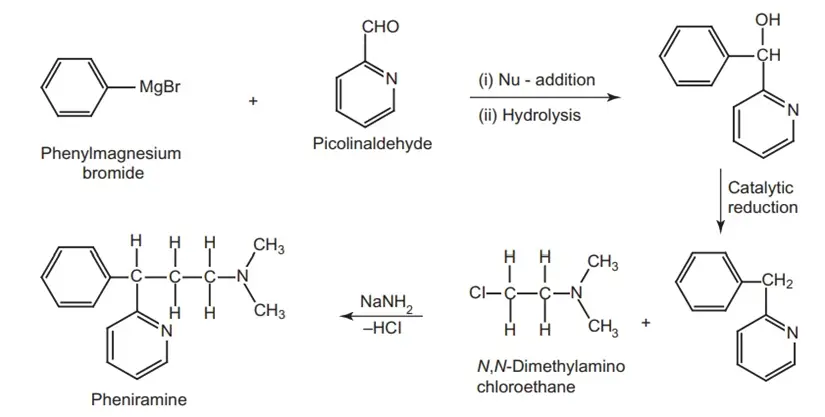
Route II. From: Picolinaldehyde
Mechanism of action
Pheniramine maleate acts by blocking the effects of histamine at H1 receptors.
Properties and uses:
Pheniramine maleate is a white crystalline powder, freely soluble in water, alcohol, methanol, and methylene chloride. This drug is the least potent member of the series and is marketed as the racemate.
Assay:
Dissolve the sample in anhydrous acetic acid and titrate against 0.1 M perchloric acid. Determine the end-point potentiometrically.
Dose:
The usual dose is 25–30 mg daily in divided doses.