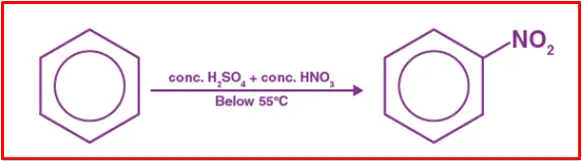
The nitration of benzene is a chemical process where benzene undergoes a reaction with concentrated nitric acid at temperatures ranging from 323 to 333 K, facilitated by the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. This reaction leads to the formation of nitrobenzene and is commonly referred to as the nitration of benzene.
Here is a step-by-step mechanism for the nitration of benzene:
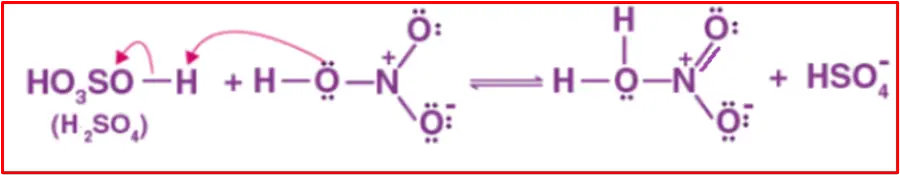
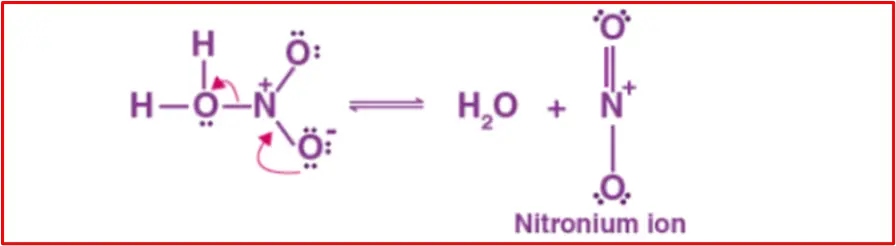
Step 1: Formation of electrophile
Nitric acid accepts a proton from sulfuric acid, forming the nitronium ion, which is crucial in the nitration of benzene.
Step 2: Formation of carbocation
The nitronium ion, acting as an electrophile, reacts with benzene to create an arenium ion intermediate.
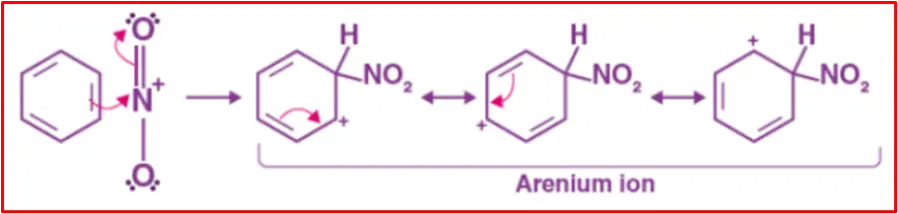
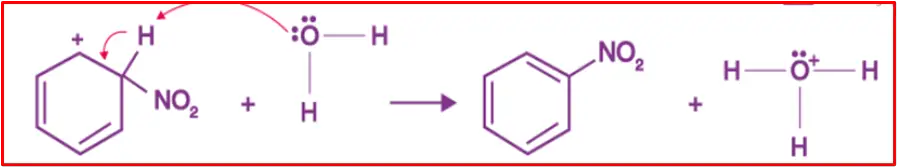
Step 3: Protonation
The arenium ion then loses its proton to Lewis’s base, forming nitrobenzene.