The nose is a multifunctional organ located on the face and serves several important roles in the human body. Its structure and functions encompass the sense of smell and the respiratory and filtration processes. Here is a detailed note on the structure and functions of the nose:
Structure of the Nose
1. External Nose:
– The external nose is the visible part of the nose, consisting of the bridge, tip, and nostrils.
– It is covered by skin and supported by cartilage, with two nostrils (nares) separated by the nasal septum.
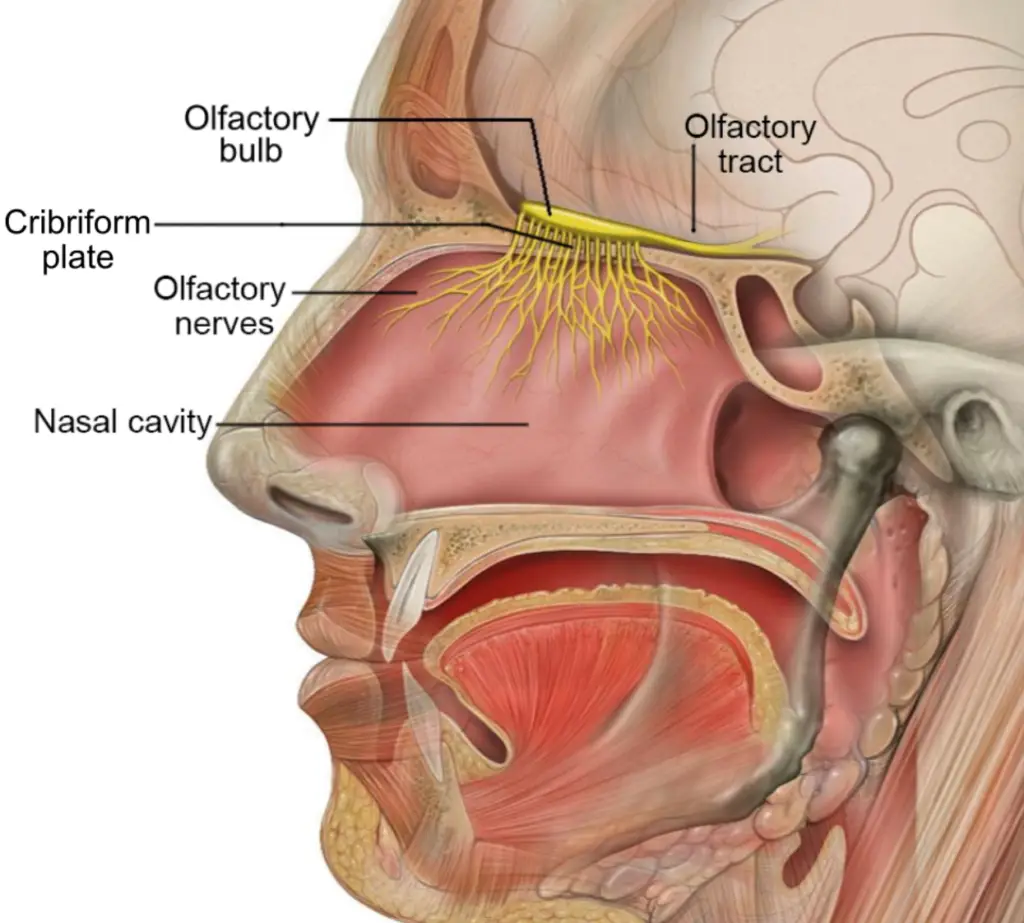
2. Internal Nose:
– The internal nose refers to the nasal cavity, a complex system of passages and structures inside the skull.
– The nasal cavity is lined with a mucous membrane containing tiny hair-like structures called cilia.
3. Sinuses:
– The paranasal sinuses are a group of air-filled cavities in the skull that connect to the nasal cavity. These include the frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid, and maxillary sinuses.
Functions of the Nose
1. Olfaction (Sense of Smell):
– The nose’s primary function is to house the olfactory epithelium, which contains olfactory receptors.
– These receptors can detect various chemical compounds in the air, allowing for the sense of smell.
2. Respiration (Breathing):
– The nose is the primary passage for air to enter the respiratory system.
– As air passes through the nasal cavity, it is warmed, humidified, and filtered, which helps protect the lower respiratory tract from harmful particles and pathogens.
3. Filtration and Cleaning:
– Nasal hairs (vibrissae) and cilia in the nasal cavity filter out particles and impurities in the inhaled air.
The mucus produced by the nasal mucosa traps dust, bacteria, and other foreign materials, preventing them from reaching the lungs.
4. Humidification:
– The nasal mucosa adds moisture to inhaled air, preventing the respiratory passages from drying.
5. Speech and Resonance:
– The nasal passages play a role in speech and voice resonance. The manipulation of airflow through the nose and mouth contributes to the articulation of sounds.
6. Temperature Regulation:
– The nose helps regulate inhaled air temperature, warming it to body temperature, which minimizes thermal shock to the lungs.
7. Immunological Defense:
– The nose contains immune cells and proteins that can help recognize and neutralize pathogens, contributing to the body’s defense against infections.
Common Nasal Disorders
1. Rhinitis: Inflammation of the nasal mucosa, often due to allergies (allergic rhinitis) or viral infections (viral rhinitis).
2. Sinusitis: Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which can lead to facial pain, congestion, and headache.
3. Nasal Polyps: Noncancerous growths in the nasal cavity or sinuses, often caused by chronic inflammation.
4. Deviated Septum: When the nasal septum is off-center or deviated, it can obstruct airflow and lead to breathing difficulties.
5. Nosebleeds (Epistaxis): Bleeding from the nose, which can result from dry air, injury, or underlying medical conditions.
6. Anosmia: Loss of the sense of smell can occur due to various factors, including nasal disorders and head injuries.