The reactions of cyclopropane and Cyclobutane are influenced by their high ring strain, leading to distinctive reactivity. Some of the notable reactions include:
(1) Addition of Cl2 & Br2: Cyclopropane reacts with Cl2 and Br2 in the dark to form additional products, using CCl4 as a solvent. The reaction does not occur with cyclobutene and any higher member.
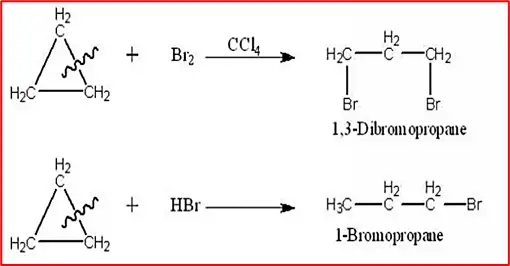
(2) Addition of HBr & HI: Cyclopropane reacts with concentrated HBr and HI to yield 1-bromopropane and 1-iodopropane, respectively. The reaction does not occur with cyclobutene and any higher member.

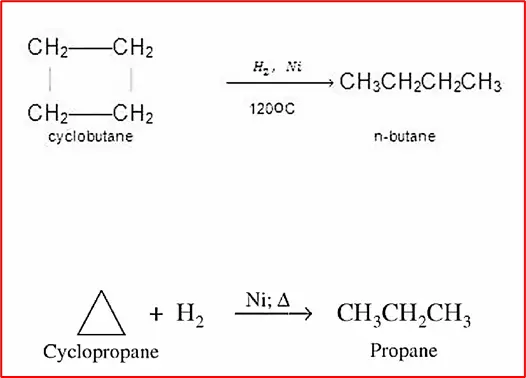
(3) Addition of hydrogen: Cyclopropane and Cyclobutane react with Hydrogen in the presence of Ni catalyst to give Propane and n-Butane, respectively. A higher temperature is required for Cyclobutane.
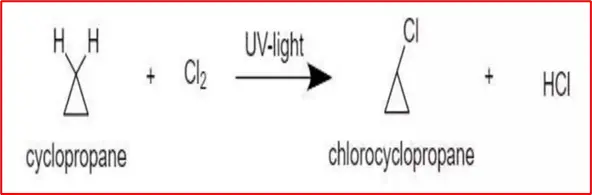
(4) Substitution with CI2 & Br2: Cyclopropane and Cyclobutane undergo substitution reactions with Cl2 and Br2 under UV light.
Due to its ring strain, Cyclobutane exhibits high reactivity, leading to various substitution and addition reactions. The high strain in these small cycloalkanes makes them more reactive than larger cycloalkanes, resulting in diverse and distinctive reaction pathways.