Suppositories are a unique form of drug delivery designed for rectal, vaginal, or urethral administration. They are solid dosage forms that melt, soften, or dissolve at body temperature, allowing the drug to be absorbed through the mucosal membranes. Suppositories are particularly useful for patients who cannot take oral medications, such as those experiencing nausea, vomiting, or difficulty swallowing.
This article delves into suppositories, their types, advantages, and limitations, while also guiding you on the correct insertion technique for a comprehensive understanding of this dosage form.
What are suppositories?
A suppository is a solid, semisolid, or molded medicated dosage form intended for insertion into the rectum, vagina, or urethra. It is composed of a drug dispersed in a base that melts or dissolves upon administration, allowing drug absorption into the bloodstream or local tissues.
Composition of Suppositories
Suppositories typically contain:
- Active pharmaceutical ingredient (API): The drug providing therapeutic action.
- Base: A carrier substance that ensures drug release (e.g., cocoa butter, polyethylene glycol, glycerinated gelatin).
- Additives: Stabilizers, preservatives, and emulsifiers to enhance stability and absorption.
Types of Suppositories
Suppositories are categorized based on their route of administration:
1. Rectal Suppositories
- Inserted into the rectum.
- Commonly used for systemic and local effects.
- Examples: Paracetamol suppositories (for fever and pain relief) and glycerin suppositories (for constipation relief).
2. Vaginal Suppositories (Pessaries)
- Inserted into the vagina.
- Primarily used for local treatment of infections, contraception, or hormone therapy.
- Examples: Clotrimazole suppositories (for yeast infections), boric acid suppositories, and progesterone suppositories (for hormonal support in pregnancy).
3. Urethral Suppositories (Bougies)
- Inserted into the urethra.
- Less common; mainly used in male patients.
- Example: Alprostadil suppositories (for erectile dysfunction).
How to Insert a Suppository Correctly
Preparation:
- Wash hands thoroughly.
- Prepare the suppository and use gloves if needed.
Insertion Techniques:
- Rectal: Lay on your side, lift one leg, and gently insert the suppository.
- Vaginal: Insert deeply using fingers or an applicator.
- Urethral: Use lubrication and follow medical guidance.
Post-Insertion Care:
- Remain still for a few minutes to ensure proper absorption.
Advantages of Suppositories
Suppositories offer several benefits compared to oral and injectable medications:
- Bypass First-Pass Metabolism: Drugs absorbed through rectal and vaginal routes avoid liver metabolism, leading to better bioavailability.
- Ideal for Patients with Swallowing Difficulties: Useful for patients who cannot take oral medications due to vomiting, unconsciousness, or surgery.
- Localized and Systemic Effects: Can provide localized relief (e.g., hemorrhoid treatment) or systemic absorption (e.g., pain relief in children).
- Minimized Gastrointestinal Irritation: Avoids irritation caused by some drugs in the stomach and intestines.
- Prolonged Drug Action: Some suppositories offer sustained release, ensuring a longer therapeutic effect.
Common Medications in Suppository Form
- Pain Relievers: Paracetamol, Ibuprofen
- Laxatives: Glycerin, Bisacodyl
- Hormonal Treatments: Progesterone
- Antifungal Medications: Clotrimazole
- Erectile Dysfunction Treatments: Alprostadil
Disadvantages of Suppositories
Despite their advantages, suppositories have some limitations:
- Patient Discomfort and Acceptability: Some patients may feel uncomfortable or hesitant using suppositories.
- Slow Drug Absorption: Compared to oral or injectable routes, absorption can be slower and variable.
- Storage Sensitivity: Some suppositories (e.g., cocoa butter-based) require cool storage to prevent melting.
- Limited Drug Suitability: Not all drugs are suitable for rectal or vaginal administration.
- Inconvenience: Administration requires privacy and hygiene considerations, which may not be ideal for all patients.
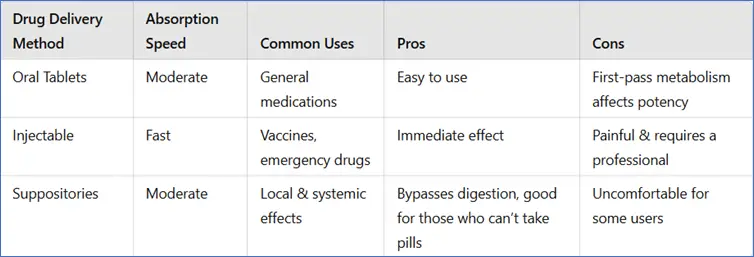
How Suppositories Compare to Other Drug Delivery Methods
Myths & Misconceptions About Suppositories
- Suppositories are only for constipation: False! They are also used for pain relief, infections, and hormonal treatments.
- They work immediately: Not always! Some take minutes, while others take hours.
- They are only for children and elderly people: False! Adults commonly use vaginal and urethral suppositories.
Conclusion
Suppositories provide a valuable alternative to oral and injectable drug delivery methods, offering systemic and local therapeutic effects. While they have advantages such as avoiding first-pass metabolism and being suitable for patients unable to take oral medications, their absorption rate, storage requirements, and patient acceptability should be considered. By understanding their types, benefits, and limitations, healthcare professionals and patients can use suppositories effectively for various medical conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are suppositories used for?
Answer: Suppositories are used to deliver medications for conditions such as pain, fever, constipation, infections, and erectile dysfunction.
2. How long does it take for a suppository to work?
Answer: The onset varies by type:
- Rectal suppositories (e.g., glycerin) act within 15-60 minutes.
- Vaginal suppositories release medication over several hours.
- Urethral suppositories work within 5-30 minutes.
3. Are suppositories better than oral medications?
Answer: Suppositories are better suited for patients who cannot take oral drugs, need localized treatment, or require drug absorption bypassing the liver.
4. Can suppositories be used daily?
Answer: Some suppositories, such as hormonal or constipation treatments, can be used regularly, but always follow medical advice.
5. How should suppositories be stored?
Answer: Suppositories should be kept in a cool, dry place (refrigeration may be needed) to prevent melting and maintain efficacy.