Suppositories are solid pharmaceutical dosage forms designed for insertion into body cavities such as the rectum, vagina, or urethra, where they melt, dissolve, or soften to deliver local or systemic therapeutic effects. A key component of suppositories is the suppository base, which acts as a carrier for the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and plays a crucial role in drug release, absorption, and patient comfort.
Choosing the right suppository base is essential for effective drug delivery, stability, and bioavailability. This comprehensive guide will explore the definition, types, advantages, disadvantages, and pharmaceutical applications of suppository bases to help you understand their role in modern drug formulations.
What are suppository bases?
A suppository base is an excipient that provides the structural framework for the suppository and facilitates drug delivery upon administration. It should have ideal characteristics such as non-irritability, good melting or dissolution properties, and compatibility with the incorporated drug.
Characteristics of an Ideal Suppository Base
A good suppository base must meet several pharmaceutical and patient-centered criteria to ensure efficacy, stability, and patient compliance. Some of the key characteristics include:
1. Melting & Dissolution Properties
- Suppositories must melt at body temperature (37°C) or dissolve in body fluids to release the drug effectively.
- Fatty bases, like cocoa butter, melt upon insertion, making them suitable for systemic absorption.
- Water-soluble bases, like polyethylene glycol (PEG), dissolve slowly in mucosal secretions, providing controlled drug release.
- The melting point should be stable across different storage conditions to avoid premature liquefaction.
2. Compatibility with Active Ingredients
- The base must be chemically and physically compatible with the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API).
- Lipophilic drugs dissolve better in hydrophilic bases (PEG, glycerinated gelatin), while hydrophilic drugs disperse well in fatty bases (cocoa butter, hydrogenated vegetable oils).
- Incompatibility can cause drug degradation, phase separation, or crystallization, affecting therapeutic effectiveness.
3. Mucosal Irritation & Patient Comfort
- A well-formulated base should be non-irritating to rectal, vaginal, or urethral mucosa.
- PEG-based suppositories may cause dehydration and irritation, whereas fatty bases offer a soothing effect.
- Additives like emollients or buffering agents can help minimize discomfort and enhance patient compliance.
4. Storage Stability & Temperature Sensitivity
- Fatty bases like cocoa butter require cool storage (below 25°C) to prevent melting.
- Water-soluble bases (PEG, glycerinated gelatin) are more stable at room temperature.
- Bases should resist microbial growth, oxidation, and polymorphic changes that can alter their performance.
Types of Suppository Bases
Suppository bases are broadly classified into three categories:
1. Fatty or Oleaginous Bases
These are hydrophobic bases composed of fatty substances that melt at body temperature to release the drug.
Examples:
- Cocoa butter (Theobroma oil) – Natural, widely used, solid at room temperature but melts at body temperature.
- Hydrogenated vegetable oils (e.g., Witepsol, Fattibase, Hard Fat) – Synthetic alternatives to cocoa butter with improved stability.
Advantages:
- Non-irritating and non-toxic.
- Good patient compliance due to smooth texture.
- Provides prolonged drug release by slow melting.
Disadvantages:
- Prone to polymorphic transitions, affecting stability.
- Melts at room temperature, requiring special storage conditions.
- Poor water-absorbing capacity.
2. Water-Soluble and Water-Miscible Bases
These bases dissolve in body fluids rather than melting, ensuring uniform drug distribution.
Examples:
- Glycerinated gelatin – Used for vaginal suppositories due to its slow dissolution and prolonged drug release.
- Polyethylene glycols (PEGs) – Synthetic polymers available in different molecular weights for tailored drug release.
Advantages:
- No special storage conditions are required.
- Provides controlled drug release.
- Less leakage compared to fatty bases.
Disadvantages:
- It may irritate due to its hygroscopic nature.
- Requires water for dissolution, delaying drug action.
3. Emulsifying or Surfactant Bases
These bases contain emulsifiers that allow better drug dispersion and absorption.
Examples:
- Massa Esterium – A blend of water-soluble and oleaginous components.
- Suppocire – A synthetic base with both hydrophilic and lipophilic properties.
Advantages:
- Suitable for both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs.
- Improves drug absorption and bioavailability.
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to traditional bases.
- Potential compatibility issues with some APIs.
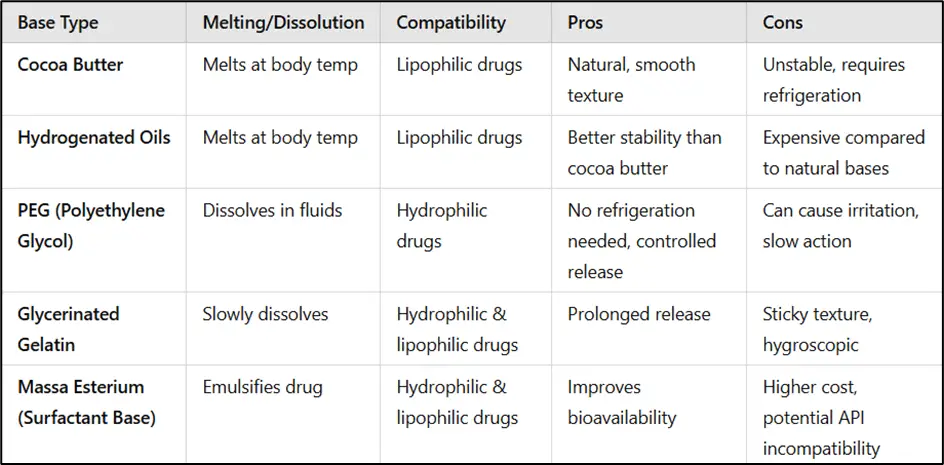
Comparison of Suppository Bases
A comparative analysis of different suppository bases can help formulators select the most suitable option based on drug compatibility, storage conditions, and patient needs.
Pharmaceutical Applications of Suppository Bases in Drug Formulations
Suppository bases are used across various pharmaceutical applications, including:
1. Rectal Suppositories: Used for local effects (e.g., hemorrhoids, inflammation) and systemic absorption (e.g., pain relief, nausea control).Example: Paracetamol suppositories for fever and pain relief.
2. Vaginal Suppositories (Pessaries): Used for antifungal, antibacterial, and hormone therapy.Example: Clotrimazole vaginal suppositories for yeast infections.
3. Urethral Suppositories (Bougies): Used for localized drug delivery in urological conditions.Example: Alprostadil urethral suppository for erectile dysfunction.
Role of Suppository Bases in Drug Release & Absorption
The choice of suppository base significantly influences drug release rate, absorption mechanism, and therapeutic efficacy.
1. How Different Bases Affect Bioavailability
- Fatty bases melt quickly and allow drug absorption through the rectal mucosa or vaginal epithelium.
- Water-soluble bases dissolve gradually, leading to a sustained-release effect.
- Drug partitioning between the base and mucosal fluids determines absorption efficiency.
2. Impact of Particle Size & Solubility on Drug Release
- Smaller particle size enhances drug dissolution and absorption.
- Lipophilic drugs in fatty bases may have slower release, whereas hydrophilic drugs in PEG bases dissolve faster.
- Surfactant-containing bases can improve drug solubility and penetration into tissues.
3. Case Studies on Effective Suppository Formulations
- Paracetamol Suppositories: Cocoa butter enhances rapid absorption for pain relief in pediatric patients.
- Progesterone Vaginal Suppositories: Glycerinated gelatin provides sustained hormone delivery for pregnancy support.
- Alprostadil Urethral Suppositories: PEG base ensures quick systemic absorption for erectile dysfunction treatment.
Innovations in Suppository Base Formulations
New technologies are transforming suppository formulations, enhancing drug solubility, stability, and patient compliance.
1. Use of Nanotechnology in Suppositories
- Nanoparticle-based suppositories improve drug solubility and targeted delivery.
- Nanoemulsions can enhance absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs.
2. Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDS)
- SEDDS-based suppositories increase drug dissolution rates, allowing better bioavailability.
- Useful for lipophilic drugs requiring enhanced solubility.
3. New Biodegradable & Mucoadhesive Bases
- Mucoadhesive suppositories prolong drug retention at the site of action, which is useful for hormonal and antimicrobial treatments.
- Biodegradable lipid-based suppositories reduce environmental impact and enhance patient safety.
How to Choose the Right Suppository Base for a Formulation
Pharmaceutical formulators must consider various factors when selecting an appropriate base for suppository formulations.
1. Factors Affecting Base Selection
- Drug Properties: Solubility, stability, and pH sensitivity influence base selection.
- Patient Needs: Age, medical condition, and route of administration dictate the ideal base.
- Therapeutic Objective: Local vs. systemic effect requires different drug release profiles.
- Manufacturing Conditions: Bases should be compatible with large-scale production and storage requirements.
2. Pharmaceutical Guidelines for Selecting Bases
- Regulatory agencies like FDA, EMA, and USP provide guidelines for suppository formulation and testing.
- Quality control tests include melting range, uniformity, drug release profile, and microbial stability.
- Industry standards recommend stability studies to assess long-term performance.
Conclusion
Suppository bases play a crucial role in drug formulation, influencing drug stability, absorption, and patient comfort. Selecting the right base is essential for ensuring effective therapeutic outcomes. Understanding the advantages, disadvantages, and applications of different bases helps pharmacists and formulators develop optimal suppository medications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the best base for rectal suppositories?
Answer: Cocoa butter and synthetic fatty bases like Witepsol are commonly used due to their rapid melting at body temperature.
2. Can polyethylene glycol (PEG) suppositories cause irritation?
Answer: Yes, PEG bases can cause irritation as they absorb moisture from mucosal tissues, leading to dehydration.
3. Why is cocoa butter less stable than synthetic fatty bases?
Answer: Cocoa butter undergoes polymorphic transitions, which can alter its melting point and reduce stability.
4. Which base is preferred for vaginal suppositories?
Answer: Glycerinated gelatin is often preferred for vaginal applications as it dissolves slowly, providing prolonged drug release.
5. Do suppository bases affect drug absorption?
Answer: Yes, the base influences drug release and absorption; fatty bases provide slower drug release, while water-soluble bases dissolve for quicker absorption.



