The preparation of 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin from resorcinol is a classical organic reaction known as the Pechmann condensation, which involves the acid-catalyzed reaction between a phenol and a β-ketoester. In this experiment, resorcinol reacts with ethyl acetoacetate in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid, acting both as a solvent and a condensing agent. The reaction proceeds via the formation of a β-hydroxy ester intermediate, which then cyclizes and dehydrates to yield the coumarin compound.
The reaction is highly dependent on temperature control, especially during the addition of reactants, to ensure high yield and product purity. The final product, 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin, is widely used as a fluorescent laser dye and as an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceutical agents such as hymecromone, an antispasmodic.
This experiment provides hands-on experience in heterocyclic compound synthesis, acid-catalyzed condensation reactions, and recrystallization purification.
Aim: To prepare and submit 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin from resorcinol.
REFERENCES:
- Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry by Brian S. Furniss, Antony J. Hannaford, Peter W. G. Smith & Austin R. Tatchell; Fifth Edition; Page No. 1193.
REQUIREMENTS
Chemicals: conc. sulphuric acid, resorcinol, ethyl acetoacetate, ice, sodium hydroxide solution (5%), sulphuric acid (2 M), and ethanol (95%).
Apparatus: Three-necked flask – 3 liters, thermometer, mechanical stirrer, dropping funnel, beaker, Buchner funnel, measuring cylinder, filter paper.
PRINCIPLE:
The synthesis of coumarins generally involves the reaction of a phenol with a β-ketoester in the presence of an acid-condensing agent, known as the Pechmann reaction. Concentrated sulfuric acid is typically used as the condensing agent for simple monohydric phenols and β-ketoesters, though phenol reacts more effectively with aluminum chloride.
The reaction mechanism is believed to start with the formation of a β-hydroxy ester, which then cyclizes and dehydrates to produce the coumarin. Polyhydric phenols, especially those with meta-oriented hydroxyl groups, react very readily. For these phenols, sulfuric acid is used as the condensing agent, with careful temperature control to ensure a good yield.
REACTION:
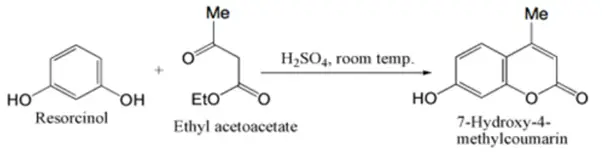
Use:
It is used commercially as a laser dye and as the starting material for producing the insecticide hymecromone’.
PROCEDURE:
- Take 1 liter of concentrated sulfuric acid in a 3-liter, three-necked flask fitted with a thermometer, mechanical stirrer, and a dropping funnel. Immerse the flask in an ice bath.
- When the temperature falls below 10°C, add a solution of 100 g (0.91 mol) of resorcinol in 134 g (130.5 ml, 1.03 mol) of redistilled ethyl acetoacetate dropwise with stirring. Maintain the temperature below 10°C using an ice-salt bath during the addition (2 hours).
- Keep the mixture at room temperature for 18 hours and pour the mixture into 2 kg of crushed ice combined with 3 liters of water, stirring vigorously.
- Collect the precipitate by suction filtration and wash it with three 25 ml portions of cold water.
- Dissolve the solid in 1500 ml of 5% sodium hydroxide solution, then filter. Add dilute 2 M sulfuric acid (about 550 ml) with vigorous stirring until the solution is acidic to litmus.
- Filter the crude 4-methyl-7-hydroxycoumarin using suction filtration, and wash the product with four 25-ml portions of cold water.
- Dry the product at 100°C and recrystallize from 95% ethanol.
- The pure compound will separate as colorless needles with a melting point of 185°C.
CALCULATION:
Here, the limiting reagent is resorcinol; hence, the yield should be calculated from the amount taken.
Molecular formula of resorcinol = C6H6O2
The molecular formula of 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin = C10H8O3
Molecular weight of resorcinol = 110 g/mole
And molecular weight of 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin = 176 g/mole
Theoretical yield:
110 g resorcinol forms 176 g 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin
Therefore, 100 g of resorcinol will form …….? (X) g 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin
= 160 g
Theoretical yield = 160 g
Practical yield = ————- g
% Yield = (Practical Yield)/(Theoretical Yield) × 100
RESULT:
7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin was synthesized from acetanilide and submitted.
| Name of Compound | 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin |
| Theoretical yield | ……gm |
| Practical yield | ……gm |
| % Practical yield | .……% |
| Melting point | .……ͦC |
How to Get Your Copy:
- Click the download link below.
- Dive into a wealth of knowledge and elevate your learning experience!
Viva voce questions
1. What is the reaction mechanism involved in the synthesis of 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin?
Answer: The reaction follows the Pechmann condensation, where resorcinol (a phenol) reacts with ethyl acetoacetate (a β-ketoester) in the presence of concentrated sulfuric acid. The reaction involves electrophilic substitution, cyclization, and dehydration steps to yield 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin.
2. What role does sulfuric acid play in this reaction?
Answer:
Sulfuric acid acts as a condensing agent and catalyst. It promotes the activation of the β-ketoester and facilitates the electrophilic attack on resorcinol, followed by cyclization and dehydration to form the coumarin ring.
3. Why is temperature control important during the addition of reagents?
Answer:
Maintaining the temperature below 10°C is crucial to prevent side reactions and decomposition. It ensures a controlled and selective reaction, increasing the yield and purity of the final product.
4. What is the use of 7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin?
Answer:
It is used as a fluorescent dye, a laser dye, and an intermediate in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals like the insecticide hymecromone. It also exhibits antioxidant and anticancer properties in medicinal chemistry.
5. How is the crude product purified after the reaction?
Answer:
The crude product is neutralized with dilute sulfuric acid, filtered, and then recrystallized from 95% ethanol to obtain pure 7-hydroxy-4-methyl coumarin as colorless needles.
🚀 Don’t miss out on this opportunity to supercharge your education. Download now and embark on a journey of continuous growth and knowledge!
Happy Learning,
pharmaacademias.com Team




