Sulphanilamide, a pioneering antibacterial agent of the sulfonamide class, played a crucial role in the early development of chemotherapeutic drugs. It inhibits bacterial growth by interfering with folic acid synthesis, making it an important historical drug in the treatment of infections. The synthesis of sulphanilamide from acetanilide is a classic example of organic transformation involving sulfonation, amidation, and hydrolysis reactions.
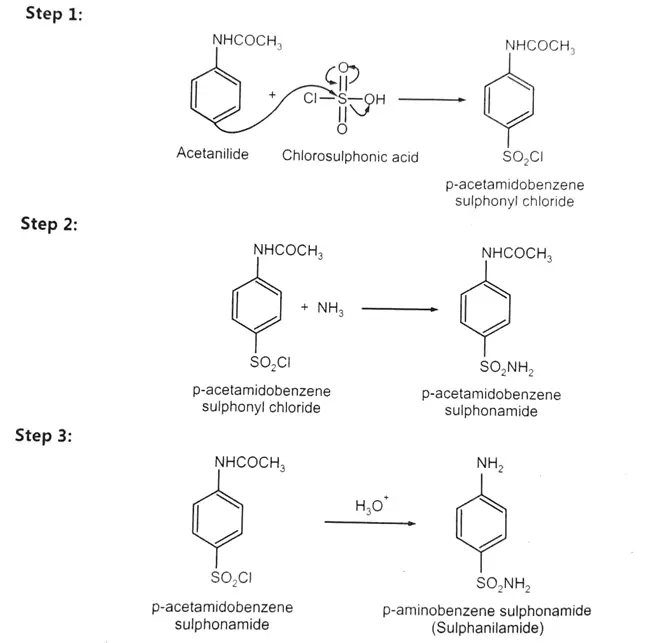
This experiment demonstrates the multi-step synthesis of sulphanilamide starting from acetanilide. The process involves three major stages: sulfonation of acetanilide with chlorosulphonic acid to form p-acetamidobenzenesulphonyl chloride, conversion of this intermediate to p-acetamidobenzenesulphonamide using ammonia, and finally, hydrolysis of the acetamido group under acidic conditions to yield sulphanilamide. This experiment not only illustrates important synthetic organic techniques like electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution but also gives hands-on experience in purification and yield calculation.
By performing this synthesis, students gain insights into the fundamental steps of drug synthesis and the transformation of simple starting materials into biologically active compounds.
Aim: To prepare and submit Sulphanilamide from acetanilide.
References:
1. Vogel’s Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry by Brian S. Furniss, Antony J. Hannaford, Peter W. G. Smith & Austin R. Tatchell; Fifth Edition: Page No. 883.
2. Practical in organic chemistry, by Hitesh G. Raval, Sunil L. Baldania and Dimal A. Shah, Nirav Prakashan, Page No. 308.
3. Indian Pharmacopoeia, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, the government of India, edition 1996, vol. II, page no. A 196.
REQUIREMENTS
Chemicals: Acetanilide, Chlorosulphonic acid, conc. ammonia, dil. sulfuric acid, sodium bicarbonate, and conc. hydrochloric acid.
Apparatus: Round-bottom flask (2000 ml), reflux condenser, beaker, Buchner funnel, measuring cylinder, and filter paper.
PRINCIPLE:
Sulphanilamide can be prepared by taking acetanilide and treating it with excess Chlorosulphonic acid. This gives p-acetamido benzene sulphonyl chloride, readily converted into corresponding p-acetamido benzene sulphonamides upon reaction with ammonia or ammonium carbonate. The acetamido groups can easily undergo an acid-catalyzed hydrolysis reaction to form p-aminobenzene sulphonamides (Sulphanilamide).
Reaction:
Procedure:
Step 1: To prepare p-acetamido benzene sulphonyl chloride:
1. Set up a 500 ml double-necked flask with a dropping funnel and a reflux condenser. Connect the top of the condenser to a hydrogen chloride absorption device. Place 20 g (0.148 mol) of dry acetanilide in the flask. Fill the dropping funnel with 50 ml (90 g, 0.77 mol) of high-grade Chlorosulphonic acid and attach a calcium chloride guard tube to the funnel.
2. Slowly add the Chlorosulphonic acid to the flask in small portions, shaking the flask occasionally to ensure thorough mixing. Once all the acid is added, heat the reaction mixture in a water bath for 1 hour to complete the reaction.
3. Allow the mixture to cool. Carefully pour the oily mixture in a thin stream into 300 g of crushed ice (or ice water) in a 1-liter beaker while stirring. Perform this step in a fume cupboard, as the excess Chlorosulphonic acid will react vigorously with the water. Rinse the flask with a small amount of ice water and add the rinse to the beaker. Break up any solid lumps and stir for several minutes until you have an even suspension of the granular white solid.
4. Filter the p-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride using a vacuum pump, wash it with cold water, and press it to drain well. Use the crude product immediately in the next stage.
Step 2: Prepare p-Acetamidobenzenesulphonamide
1. Transfer the crude p-acetamidobenzenesulphonyl chloride to the rinsed reaction flask. Add a mixture of 70 ml of concentrated ammonia solution and 70 ml of water to the flask. Mix the contents well and heat the reaction mixture with occasional swirling in a fume cupboard until it is just below boiling for about 15 minutes. During this time, the sulphonyl chloride will convert into a pasty suspension of the corresponding sulphonamides.
2. Cool the product suspension in ice, then add dilute sulfuric acid until the mixture is just acidic to Congo red paper. Collect the product using a Buchner funnel, wash with a little cold water, and drain as thoroughly as possible. While it is desirable, but not essential, to dry the crude p-acetamidobenzenesulphonamide at 100°C, the yield is about 18 g. This material is sufficiently pure for the next stage.
Step 3: To prepare p-aminobenzenesulphonamide
1. Transfer the crude p-acetamidobenzenesulphonamide to a 500 ml flask. Mix 10 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid with 30 ml of water and add this mixture to the flask. Boil the mixture gently under reflux for 30-45 minutes. Then, cool the solution to room temperature. Ensure no solid amide is deposited; if a solid form, heat for a short additional period.
2. Once the solution is cooled, add 2 g of decolorizing carbon, heat the mixture to boiling, and filter it with suction through hardened filter paper. Transfer the filtrate, which contains a solution of sulfanilamide hydrochloride, to a 1-liter beaker. Carefully add 16 g of solid sodium hydrogen carbonate in portions, stirring constantly. After the gas evolution subsides, test the suspension with litmus paper. If it is still acidic, add more sodium hydrogen carbonate until neutral.
3. Cool the mixture in ice, then filter off the sulfanilamide with suction and dry it. The yield is approximately 15 g (59% overall), with a melting point of 161-163°C. A pure product with a melting point of 163-164°C can be obtained by recrystallization from water or alcohol.
Calculation:
The limiting reagent is acetanilide; the yield should be calculated from the amount taken.
Molecular formula of acetanilide = C8H9NO
The molecular formula of sulphanilamide = C6H8N2O2S
The Molecular weight of acetanilide = 135 g/mole Molecular weight of sulphanilamide = 172 g/mole
Theoretical yield:
135 g acetanilide forms 172 g sulphanilamide
Therefore, 20 g acetanilide will form …….? (X) g sulphanilamide
X =(172 ×20)/135 = 25.48 g
Theoretical yield = 25.48 g
Practical yield = ————- g
% Yield = (Practical Yield)/(Theoretical Yield) × 100
Result:
Sulphanilamide was synthesized from acetanilide and submitted.
| Name of Compound | Sulphanilamide |
| Theoretical yield | ……gm |
| Practical yield | ……gm |
| % Practical yield | .……% |
| Melting point | .……ͦC |
🚀 Don’t miss out on this opportunity to supercharge your education. Download now and embark on a journey of continuous growth and knowledge!
Happy Learning,
pharmaacademias.com Team



