Introduction:
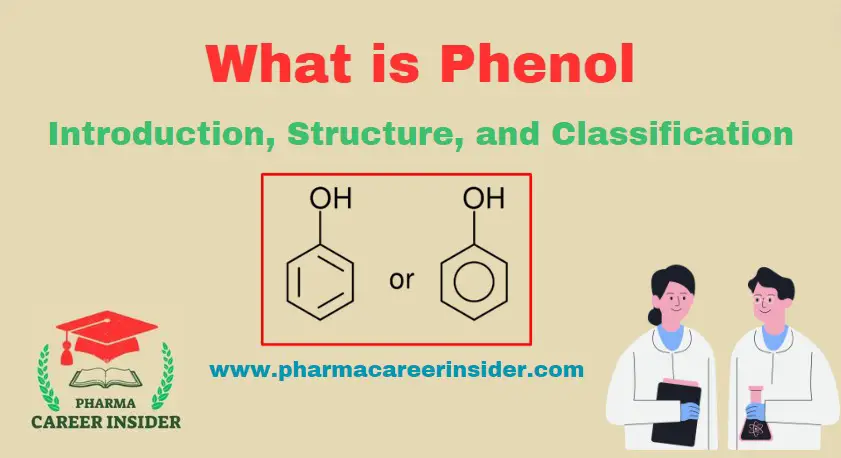
Phenol, or carbolic acid, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. The molecule consists of a phenyl group (−C6H5) bonded to a hydroxy group (−OH). Phenol is a white crystalline solid at room temperature with a distinctive sweet and medicinal odor. It was one of the first antiseptics used in medicine and is the precursor to various chemical compounds and polymers.

In phenol, the hydroxy functional group is directly attached to the sp2 hybridized carbon atom of the benzene ring. The interaction of six unhybridized 2pz orbitals of carbon atoms of the benzene ring leads to the formation of delocalized pi-electron clouds. The C-O-H bond angle in phenol is 1090. The carbon-oxygen bond length (136pm).
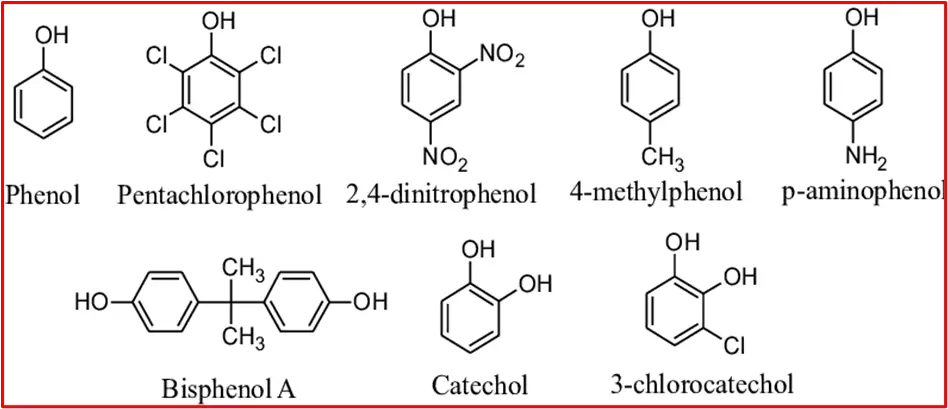
Here are some examples of phenol compounds:
Classification of Phenol:
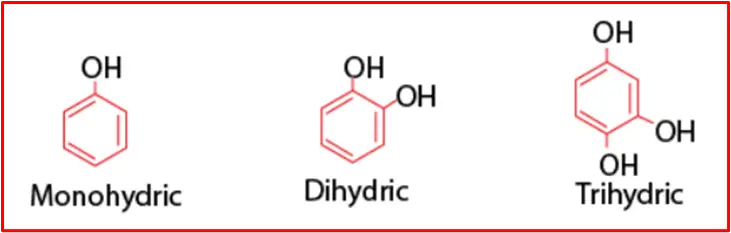
Phenols can be categorized into three types based on the number of hydroxyl groups attached:
1. Monohydric Phenols: This type features phenols with a single -OH group.
2. Dihydric Phenols: Phenols in this category have two -OH groups, which may exist as ortho-, meta-, or para-derivatives.
3. Trihydric Phenols: This type encompasses phenols containing three -OH groups.