A receptor is a specialized protein molecule, typically found on the surface of a cell or within its interior, that is capable of binding to specific signaling molecules called ligands. Receptors play a crucial role in cellular communication and signal transduction, serving as molecular switches that initiate cellular responses to extracellular stimuli.
Or
Receptor is a protein molecule that receives chemical signals from outside a cell. When such chemical signals bind to a receptor, they cause some form of cellular/tissue.

There are several types of receptors, each with its own specific characteristics and functions:
Cell Surface Receptors:
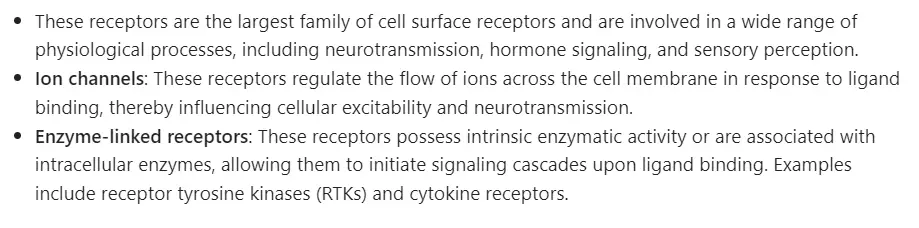
These receptors are located on the cell membrane and are involved in transmitting signals from extracellular ligands into the cell. Cell surface receptors include:
G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs):
Intracellular Receptors:
These receptors are located inside the cell, typically in the cytoplasm or nucleus, and are activated by ligands that can diffuse across the cell membrane. Intracellular receptors include:

Upon ligand binding, receptors can undergo conformational changes that lead to the initiation of intracellular signaling cascades, ultimately resulting in cellular responses. The such as gene transcription, protein synthesis, changes in ion flux, or alterations in cellular metabolism. The specificity and affinity of receptor-ligand interactions are crucial for determining the physiological outcomes of cellular signaling pathways.
Conclusion
Overall, receptors serve as molecular sensors that enable cells to respond to their environment and coordinate complex physiological processes. The ranging from neurotransmission and hormone signaling to immune responses and cell growth.