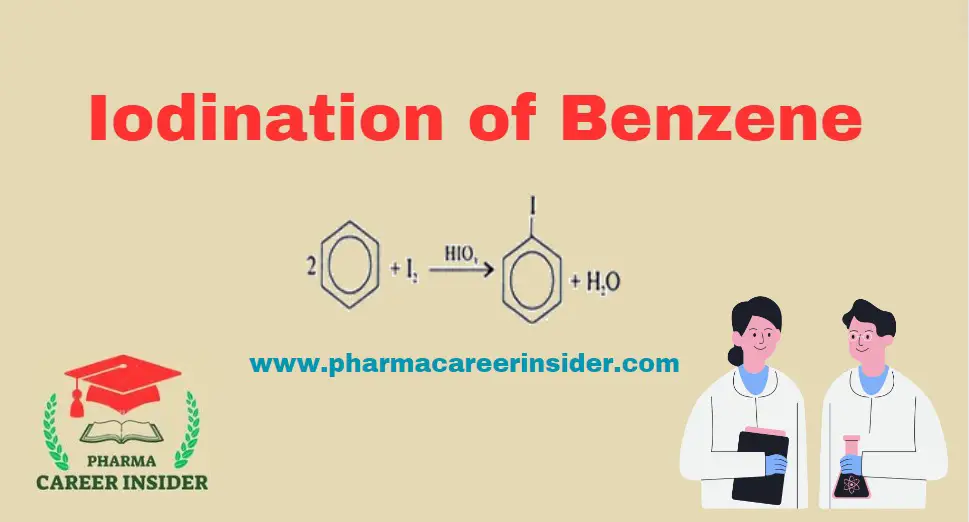
Iodination of Benzene
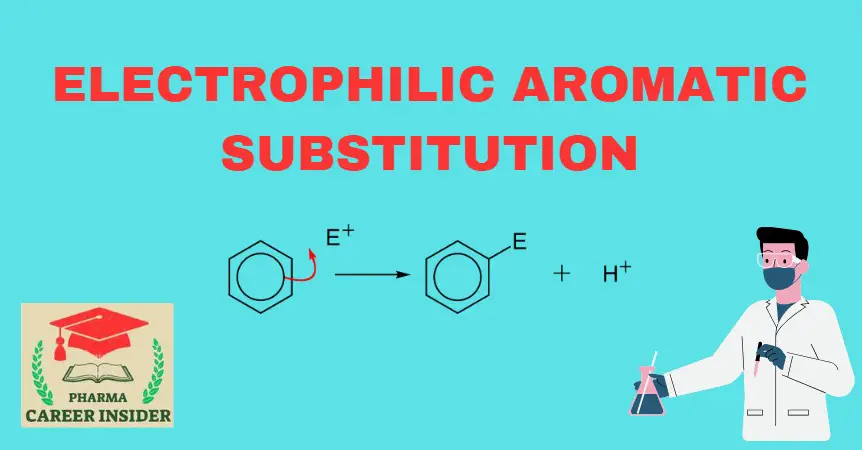
The iodination of benzene involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with an iodine atom through an electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) reaction. Here is the reaction with a concise explanation: Here is a step-by-step mechanism for the iodination of benzene: Step 1: Formation of electrophile Iodine reacts with iodic acid (HIO3)to … Read more