Phenanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) composed of three fused benzene rings, resulting in a bicyclic structure. It is a colorless crystalline solid at room temperature naturally found in coal tar, crude oil, and various fossil fuels. Phenanthrene is a prominent PAH family member and is a fundamental building block in organic chemistry and various industrial applications.
Chemical Structure:
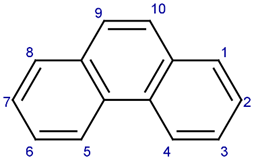
Phenanthrene’s molecular formula is C14H10, and its structure consists of three benzene rings fused in a linear arrangement. The molecule is planar, with each carbon atom bonding aromatic and sigma. It exhibits aromaticity due to the delocalization of pi-electrons across the entire molecule.
Occurrence:
Phenanthrene occurs naturally in fossil fuels like coal, petroleum, and shale oil. It is formed during the incomplete combustion of organic matter, contributing to its presence in environmental matrices like soil, water, and air. Phenanthrene is also produced as a byproduct of various industrial processes, including coal gasification, oil refining, and combustion of organic materials.
Applications:
1. Organic Synthesis: Phenanthrene serves as a versatile precursor in organic synthesis, enabling the construction of complex molecules with aromatic scaffolds. It participates in numerous reactions, including cyclization, oxidation, and halogenation, to produce functionalized derivatives in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and materials science.
2. Analytical Chemistry: Phenanthrene is employed as a reference compound in analytical chemistry techniques, particularly chromatography and spectroscopy.
3. Research: Due to their environmental and biological significance, phenanthrene and its derivatives are subjects of extensive research.
4. Industrial Processes: Phenanthrene finds utility in various industrial processes, including producing dyes, pigments, and specialty chemicals. Phenanthrene’s unique structure and chemical properties make it a valuable compound in organic synthesis, analytical chemistry, research, and industrial applications. Its widespread occurrence and versatile reactivity underscore its significance in natural and synthetic contexts.
Meta Description
Discover phenanthrene, a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with diverse applications in organic synthesis, analytical chemistry, and industrial processes. Learn about its molecular structure, natural occurrence in fossil fuels, and role as a fundamental building block in organic chemistry. Explore phenanthrene’s versatile reactivity and significance in both natural and synthetic contexts.

