1. Promethazine HCl (Phenargen)
Promethazine HCl is a versatile medication within the phenothiazine class, acclaimed for its multifaceted pharmacological properties. As an antagonist at H1 histamine receptors, it effectively mitigates allergic symptoms, while its antimuscarinic actions contribute to potent antiemetic effects. Widely utilized to alleviate symptoms ranging from allergic reactions to motion sickness and nausea, promethazine HCl is available in diverse formulations, including tablets, syrups, and suppositories.
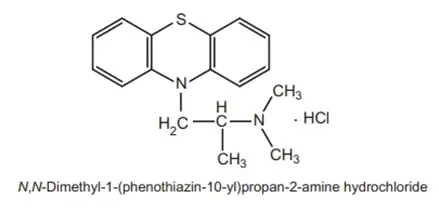
Structure
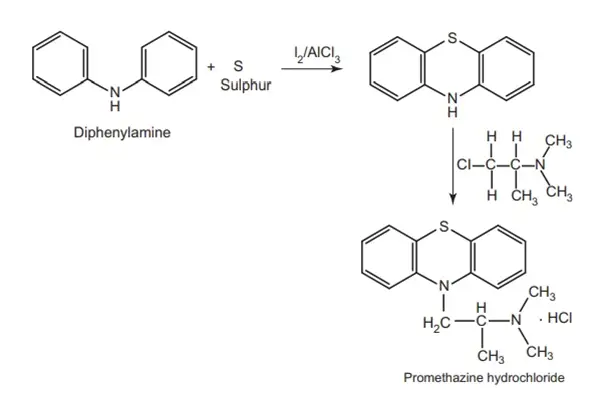
Synthesis
Mechanism of action
The primary mechanisms of action include:
- H1 Histamine Receptor Antagonism:
- Promethazine acts as an antagonist at H1 histamine receptors, blocking the effects of histamine.
- This action helps alleviate symptoms associated with allergic reactions, such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose.
- Antimuscarinic (Anticholinergic) Activity:
- Promethazine possesses antimuscarinic properties, inhibiting the activity of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors.
- This contributes to its antiemetic effects, helping to prevent and relieve nausea and vomiting.
- Dopamine Receptor Blockade:
- As a phenothiazine derivative, promethazine blocks dopamine receptors to some extent.
- While this action’s clinical significance is less pronounced than other phenothiazines, it may contribute to the overall therapeutic profile.
Properties and uses:
Promethazine hydrochloride is a white or faintly yellowish crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, alcohol, and methylene chloride. Promethazine is effective for perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, allergic conjunctivitis from inhalant allergens and foods, and milder skin manifestations of urticaria. It also possesses some anticholinergic, antiserotonergic, and marked local anesthetic properties.
Assay:
Dissolve the sample in a mixture of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid and alcohol and titrate against 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Determine end point potentiometrically.
Dose:
Usual dose is 20–50 mg per day.
Dosage forms:
Promethazine hydrochloride injection I.P., Promethazine hydrochloride tablets I.P., B.P., Promethazine hydrochloride syrup I.P., Promethazine injection B.P., promethazine oral solution B.P.