Introduction
An acid-base titration is a quantitative analytical technique used to determine the concentration of an unknown acid or base by reacting it with a standard solution of known concentration. The process is based on the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base, which produces salt and water. The endpoint is usually detected using a pH indicator or a pH meter.
Basic Principle of Acid-Base Titration
The principle of acid-base titration is based on the neutralization reaction:
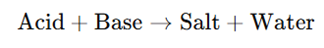
- A strong acid completely ionizes in solution (e.g., HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻).
- A strong base completely dissociates into its ions (e.g., NaOH → Na⁺ + OH⁻).
- The reaction continues until an equivalence point is reached, where moles of H⁺ = moles of OH⁻.
The concentration of the unknown solution can be calculated using the formula:

Types of Acid-Base Titration
Acid-base titrations are classified based on the strength of the acid and base involved:
1. Strong Acid vs. Strong Base
- Example: HCl (Hydrochloric acid) vs. NaOH (Sodium hydroxide)
- pH at equivalence point: 7
- Indicator: Phenolphthalein or Methyl orange
- Sharp endpoint due to complete neutralization.
2. Strong Acid vs. Weak Base
- Example: HCl (Strong acid) vs. NH₃ (Ammonia, weak base)
- pH at equivalence point: Less than 7 (acidic)
- Indicator: Methyl orange
- The weak base does not completely neutralize, leaving the solution slightly acidic.
3. Weak Acid vs. Strong Base
- Example: CH₃COOH (Acetic acid, weak acid) vs. NaOH (Strong base)
- pH at equivalence point: Greater than 7 (basic)
- Indicator: Phenolphthalein
- The weak acid does not completely react, making the final solution slightly basic.
4. Weak Acid vs. Weak Base
- Example: CH₃COOH (Weak acid) vs. NH₃ (Weak base)
- pH at equivalence point: Varies, usually neutral or slightly acidic/basic
- Indicator: No sharp endpoint; pH meter is preferred
- Difficult to perform due to gradual pH changes.
Indicators Used in Acid-Base Titrations
Indicators are chosen based on the expected pH at the equivalence point:
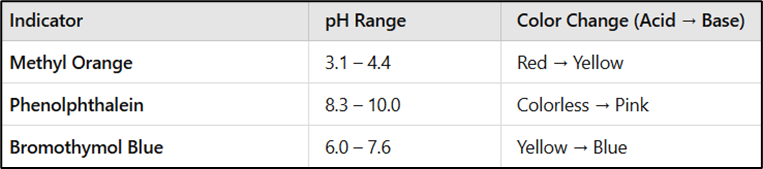
For more accurate results, a pH meter can be used instead of indicators.
Procedure for Acid-Base Titration
1. Preparation of Solutions
- Prepare a standard solution of known concentration (e.g., NaOH for titrating acids).
- Pipette a known volume of the unknown solution into a conical flask.
2. Addition of Indicator
- Add 2-3 drops of a suitable pH indicator to the acid/base solution in the conical flask.
3. Titration Process
- Fill a burette with the standard solution (e.g., NaOH).
- Slowly add the titrant dropwise while swirling the flask.
- Observe the color change of the indicator.
4. Endpoint Determination
- The endpoint is the point where the indicator changes color, signaling neutralization.
- Record the burette reading to determine the volume of titrant used.
5. Calculation of Unknown Concentration
Use the formula:
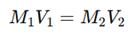
Substituting the values, we can determine the unknown molarity of the acid or base.
Sources of Error and Precautions
- Burette reading accuracy: Always read at eye level to avoid parallax errors.
- Proper mixing: Swirl the flask while adding titrant to ensure a complete reaction.
- Choice of Indicator: Use an appropriate indicator based on the type of acid and base.
- Avoid Over-Titration: Add titrant dropwise near the endpoint to prevent overshooting.
Applications of Acid-Base Titration
- Pharmaceutical Analysis: Used to determine the purity and concentration of drugs.
- Food Industry: Measures the acidity or alkalinity of food products like vinegar and fruit juices.
- Water Quality Testing: Determines the pH and alkalinity of drinking water and industrial effluents.
- Chemical Industry: Used in the manufacturing and quality control of acids, bases, and buffers.
Conclusion
Chemists use acid-base titration as a highly precise method in chemical analysis, pharmaceuticals, environmental testing, and food quality control. Proper techniques, indicators, and calculations ensure accurate and reliable results.