Meta Description
Learn about ammonium chloride as an acidifier, its preparation, properties, medicinal uses, and industrial applications. Discover its role in urinary acidification, digestion, and pH regulation.
Introduction
Ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) is a widely used inorganic acidifier with applications in medicine, industry, and agriculture. As an acidifier, it helps regulate pH levels in biological systems, particularly in urinary acidification, metabolic balance, and digestive health. In pharmaceuticals, it is used to acidify urine, enhance drug excretion, and restore acid-base balance in conditions like metabolic alkalosis. It also plays a role in food processing, animal nutrition, and industrial applications.
This article explores the preparation, properties, and role of ammonium chloride as an acidifier, highlighting its medicinal and industrial significance.
Preparation of Ammonium Chloride
Ammonium chloride is synthesized through chemical reactions between ammonia and acids. The most common methods include:
1. Reaction of Ammonia with Hydrochloric Acid
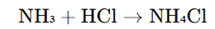
In this reaction, gaseous ammonia (NH₃) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form ammonium chloride, which is then crystallized and purified.
2. By-Product of the Solvay Process
In industrial settings, ammonium chloride is obtained as a by-product during the manufacture of sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃):

The ammonium chloride is separated, crystallized, and refined for commercial use.
Properties of Ammonium Chloride
- Chemical Formula: NH₄Cl
- Molecular Weight: 53.49 g/mol
- Appearance: White crystalline powder
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water; forms an acidic solution
- pH in Aqueous Solution: 4.5–6.0 (acidic)
- Melting Point: 338°C (sublimes without decomposition)
- Odor: Odourless but emits ammonia when heated
Ammonium chloride is a highly effective acidifier, making it suitable for urinary acidification, metabolic regulation, and pH control in various applications.
Role of Ammonium Chloride as an Acidifier
Ammonium chloride functions as an acidifier by lowering pH levels in different biological and industrial processes. Some of its key roles include:
1. Urinary Acidifier
- – Used in treating urinary tract infections (UTIs) to increase urine acidity, which helps prevent bacterial growth.
- – Promotes urinary excretion of weakly basic drugs, aiding in drug detoxification and elimination.
- – It helps in conditions like uric acid kidney stones, where urine acidification is necessary to dissolve crystals.
2. Treatment of Metabolic Alkalosis
- – In cases of metabolic alkalosis, where blood pH is excessively high, ammonium chloride lowers pH and restores normal acid-base balance.
- – Administered orally or intravenously under medical supervision.
3. Digestive and Systemic Acidification
- Used in veterinary medicine and animal feed to enhance digestion and prevent urinary calculi in livestock.
- In humans, it helps in treating hypochlorhydria (low stomach acid), improving digestion and nutrient absorption.
4. pH Control in Industrial Applications
- In food processing, ammonium chloride is used as a pH regulator in certain baked goods and confectionery.
- In textile and leather industries, it helps maintain the acidity required for dyeing and tanning processes.
Assay of Ammonium Chloride
The purity of ammonium chloride is determined using a precipitation titration method with silver nitrate (AgNO₃):
Procedure:
- – Dissolve a sample of ammonium chloride in distilled water.
- – Add nitric acid to maintain an acidic environment.
- – Titrate with standard silver nitrate (AgNO₃) solution, using potassium chromate (K₂CrO₄) as an indicator.
- – The endpoint is reached when a red precipitate of silver chromate (Ag₂CrO₄) forms, indicating a complete reaction of chloride ions.
This assay ensures accurate quantification of ammonium chloride in pharmaceutical and industrial products.
Medicinal Uses of Ammonium Chloride as an Acidifier
1. Expectorants in Cough Syrups: Stimulates bronchial secretions, helping to clear mucus in respiratory conditions like bronchitis and pneumonia. Commonly included in cough syrups and mucolytic agents.
2. Diuretic and Urinary Acidifier: Increases urinary acidity, preventing bacterial overgrowth and kidney stone formation. Used in urinary drug elimination to enhance the excretion of alkaline drugs.
3. Treatment for Electrolyte Imbalance: Administered in cases of chloride deficiency, ensuring proper acid-base balance in the body. Helps manage conditions like hyperchloremic alkalosis.
Other Applications of Ammonium Chloride: Apart from its use as an acidifier, ammonium chloride is widely used in various industries:
- – Fertilizers: Used as a nitrogen source in agriculture.
- – Food Industry: Acts as a pH regulator and flavor enhancer in certain foods.
- – Metal Processing: Helps in soldering, galvanizing, and electroplating.
- – Textile and Leather Industry: Aids in dyeing and tanning processes.
- – Battery Manufacturing: Used in dry cell batteries as an electrolyte.
Side Effects and Precautions
While ammonium chloride is beneficial, excessive intake may cause:
- 1. Gastrointestinal Distress: Nausea, vomiting, or stomach discomfort.
- 2. Metabolic Acidosis: Excess acid buildup leading to fatigue, confusion, and shortness of breath.
- 3. Electrolyte Imbalance: May alter sodium and potassium levels, affecting nerve and muscle function.
- 4. Respiratory Irritation: Inhalation of ammonium chloride dust can cause coughing and throat irritation.
Precaution: Patients with kidney disease, hypertension, or respiratory disorders should consult a doctor before using ammonium chloride-based medications.
Conclusion
Ammonium chloride is a versatile acidifier with crucial applications in medicine, food processing, animal nutrition, and industry. Its ability to lower pH levels, enhance digestion, and support urinary acidification makes it a valuable compound in pharmaceuticals. Additionally, its use in metal processing, textiles, and fertilizers highlights its industrial significance. While highly effective, careful dosage and monitoring are essential to prevent adverse effects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How does ammonium chloride act as an acidifier?
Answer: Ammonium chloride lowers pH levels in the body and industrial processes by releasing chloride ions, which increase acidity and regulate metabolic balance.
2. What are the medicinal uses of ammonium chloride?
Answer: It is used as a urinary acidifier, expectorant, diuretic, and metabolic regulator to treat conditions like UTIs, cough, and metabolic alkalosis.
3. Is ammonium chloride safe for daily use?
Answer: When used as prescribed, ammonium chloride is safe. However, excessive use can cause stomach irritation, metabolic acidosis, and electrolyte imbalances.