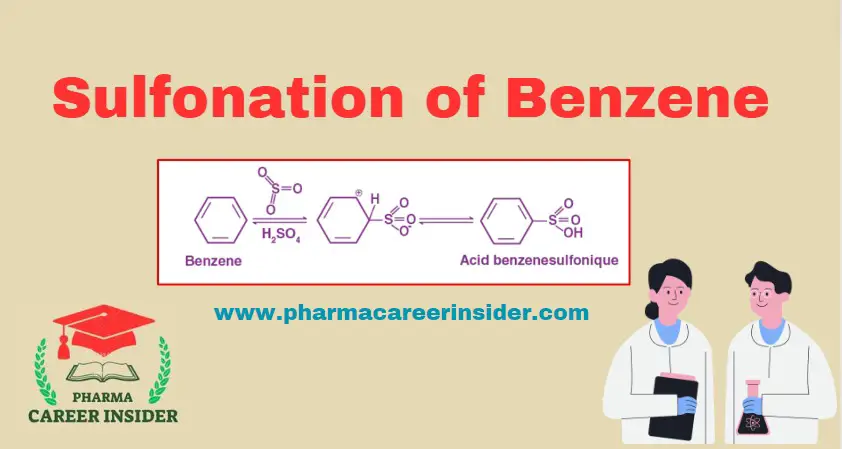
Sulfonation of benzene involves heating benzene with fuming sulfuric acid (H2SO4 + SO3) to yield benzenesulfonic acid. This reaction is reversible in nature. Here is the reaction with a concise explanation:
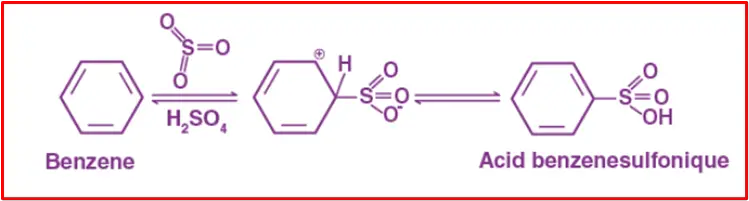
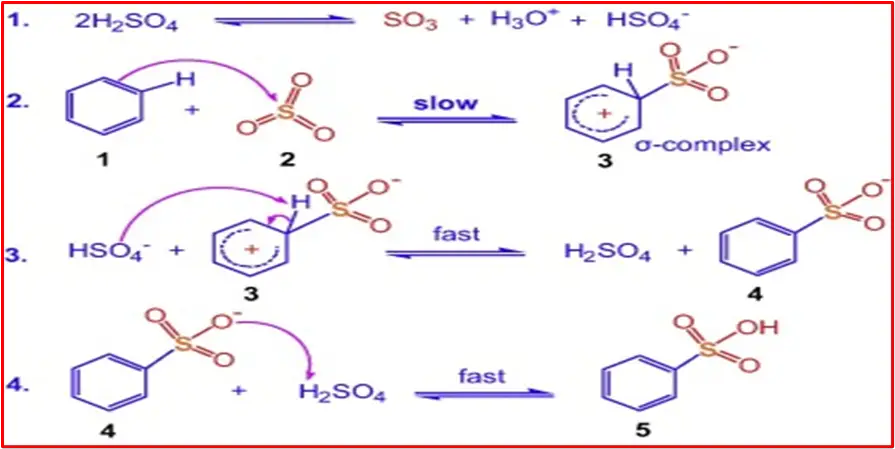
Here is a step-by-step mechanism for the sulphonation of benzene:
Step 1: Formation of electrophile
Sulphur trioxide (SO3) reacts with sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to generate the electrophile, the HSO4− ion.
Step 2: Formation of carbocation
The electrophile HSO4− attacks the benzene ring, forming a sigma complex.
Step 3: Formation of Sigma Complex
The attack forms a sigma complex, where one carbon in the benzene ring becomes temporarily sp3 hybridized.
Step 4: Protonation
A proton is lost from the sigma complex, leading to the formation of benzenesulfonic acid.