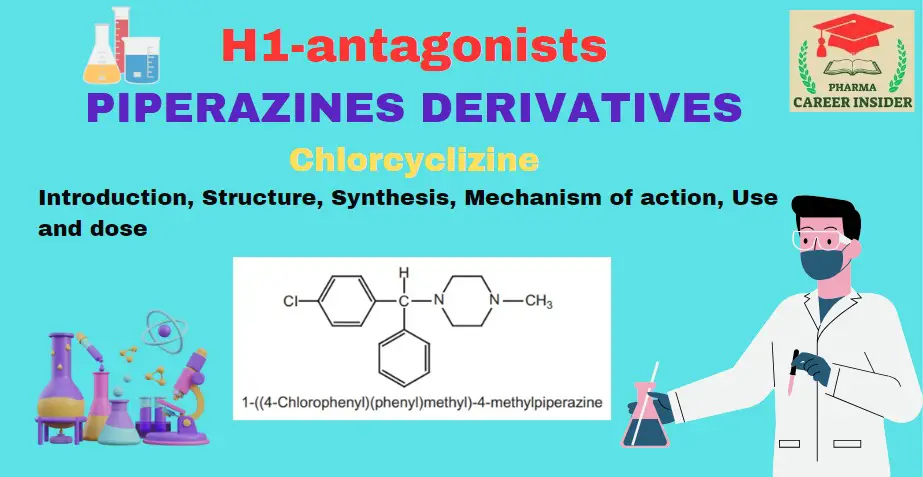
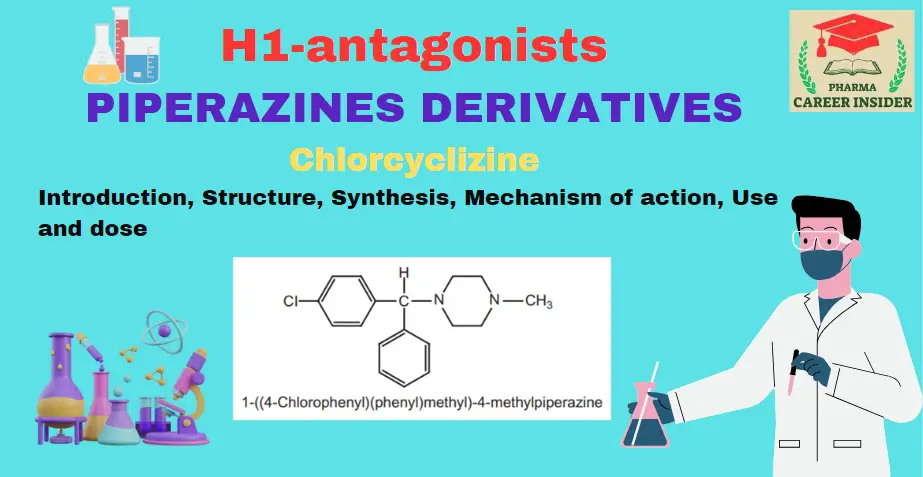
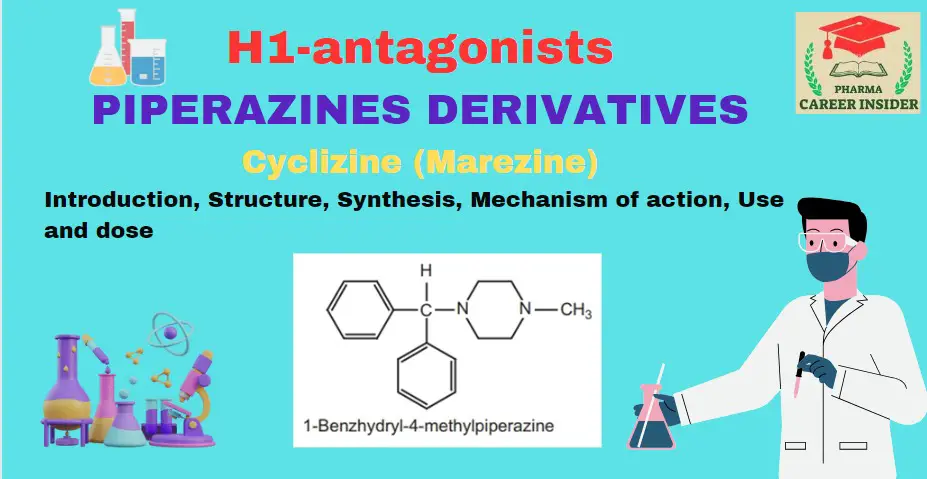
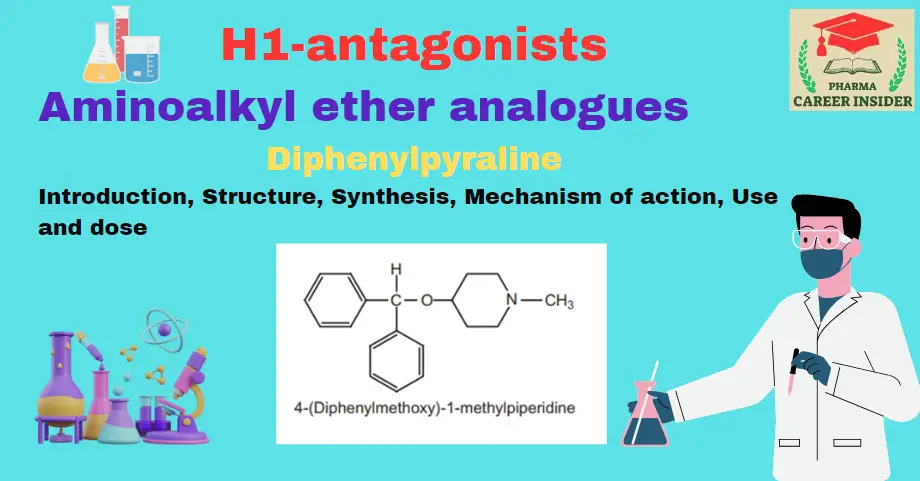
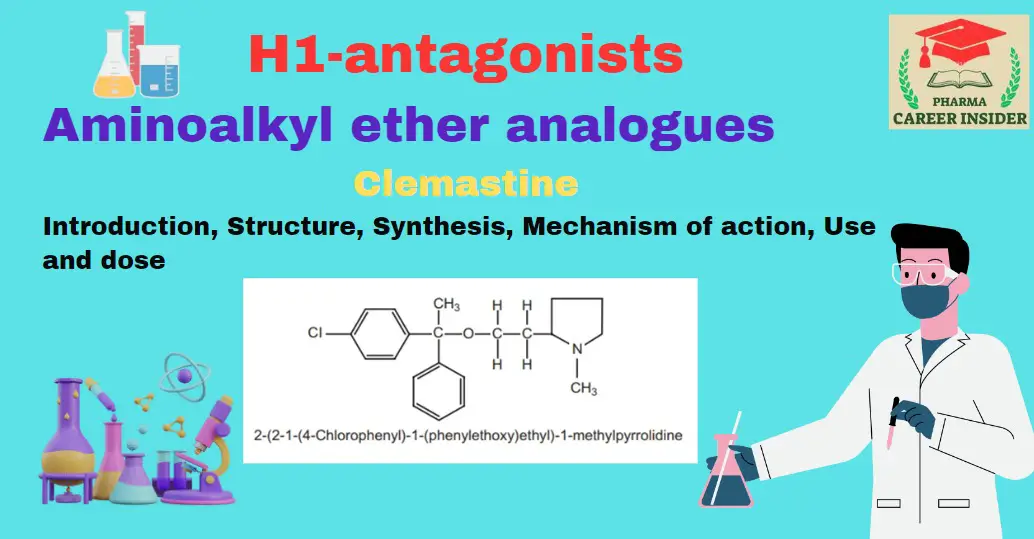
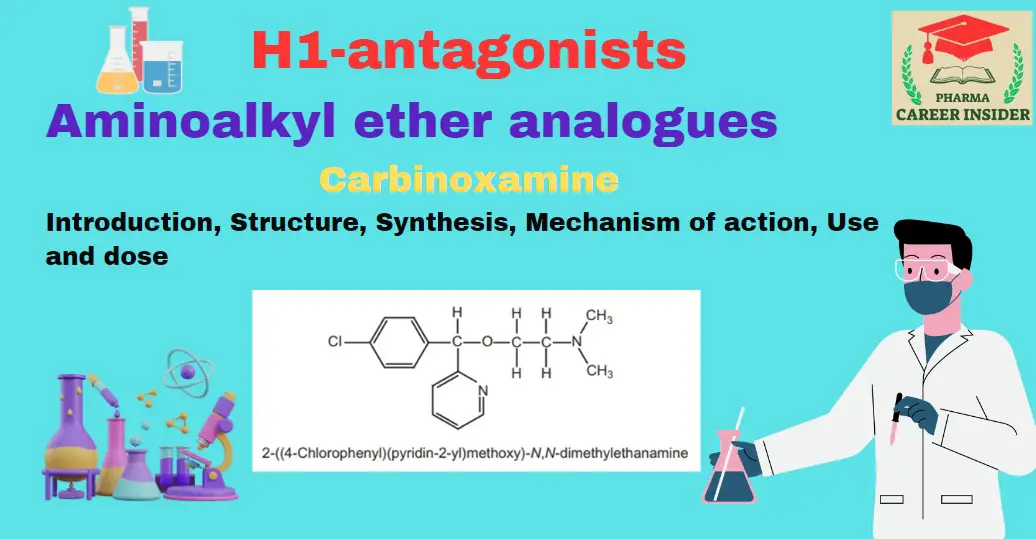
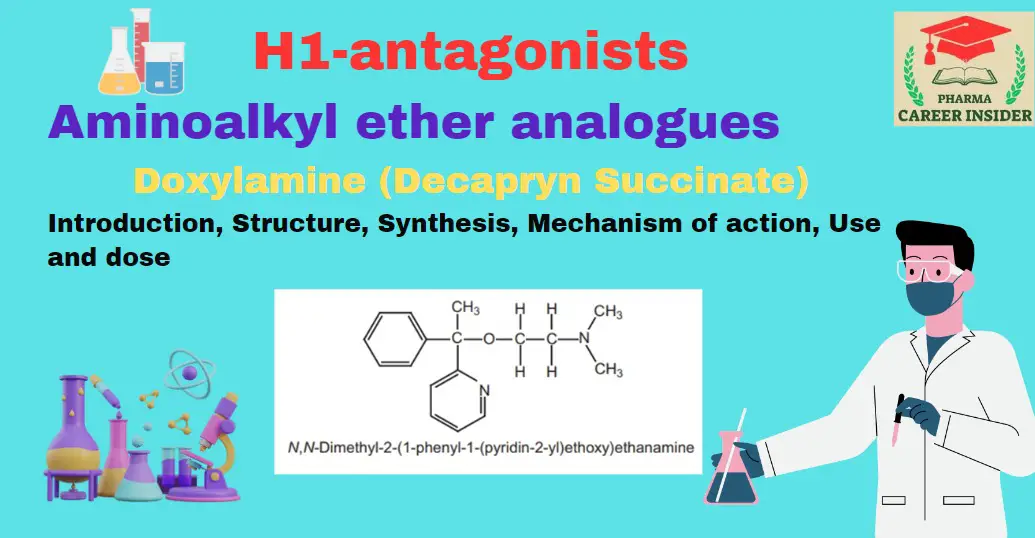
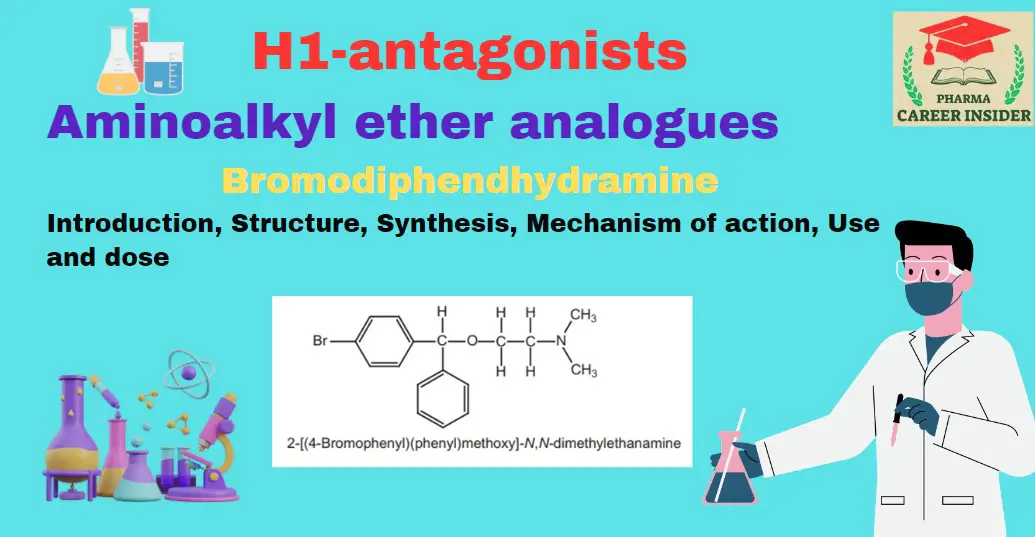
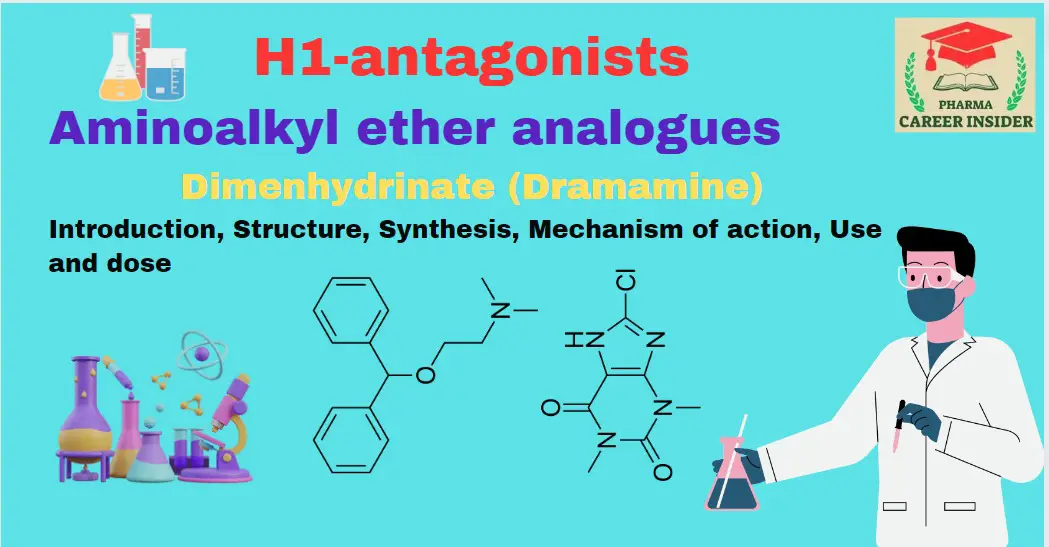
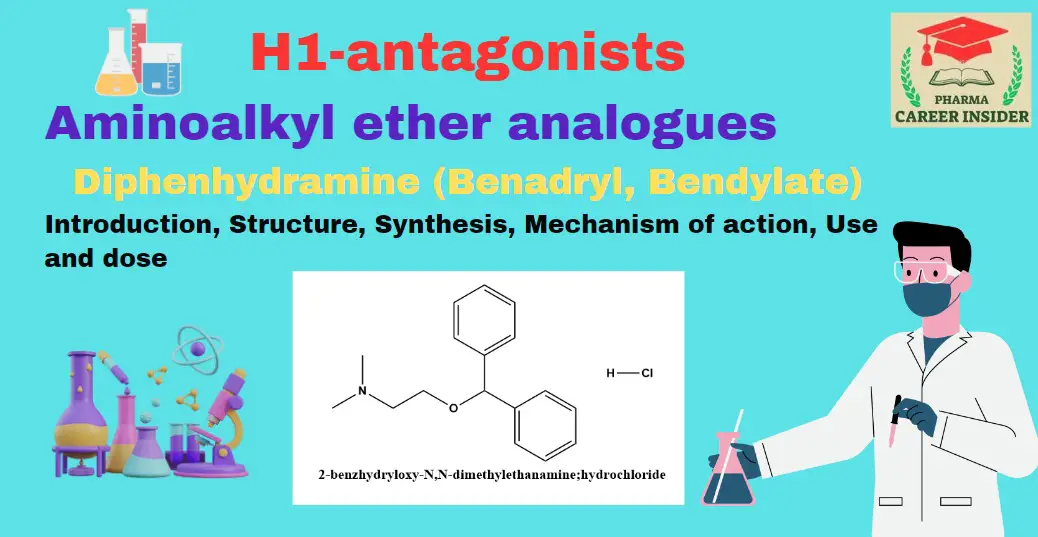
Meclizine
Introduction Meclizine is a widely used antihistamine known for its efficacy in preventing and alleviating symptoms associated with motion sickness. As an H1 receptor antagonist, it blocks the effects of histamine, providing relief from nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. Meclizine’s additional antimuscarinic properties contribute to its effectiveness as an antiemetic. Structure Synthesis Mechanism of action Meclizine’s … Read more