Introduction:
Diphenylpyraline is an antihistamine used to relieve allergy symptoms. As a first-generation antihistamine, it works by blocking the effects of histamine at the H1 receptors, providing relief from symptoms such as itching, sneezing, and runny nose associated with allergic reactions. Diphenylpyraline may also have sedative effects due to its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, and it is commonly found in over-the-counter allergy medications. As with any medication, it’s important to use diphenylpyraline under the guidance of a healthcare professional, taking into consideration individual health conditions and potential interactions.
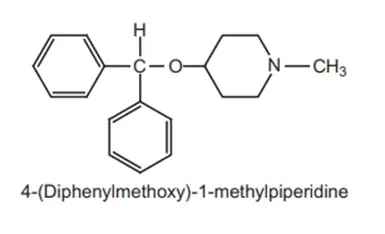
Structure:
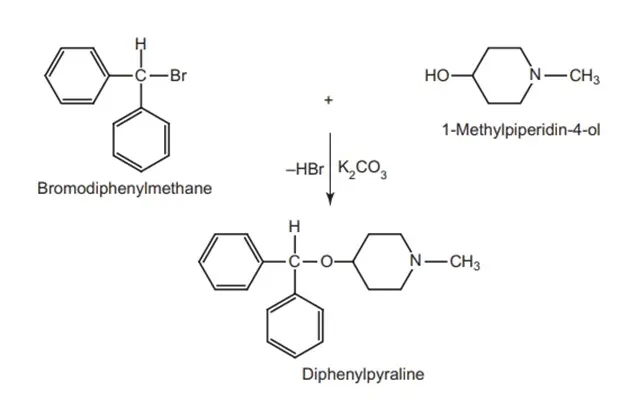
Synthesis
Mechanism of action:
Diphenylpyraline is a first-generation antihistamine with a mechanism of action that involves blocking the effects of histamine at the H1 receptors. Here’s a breakdown of its mechanism:
- Histamine Receptor Antagonism:
- Diphenylpyraline competes with histamine for binding to the H1 receptors.
- By blocking these receptors, it prevents histamine from exerting its effects.
- Reduction of Histamine Effects:
- When released during allergic reactions, Histamine can lead to symptoms like itching, sneezing, and a runny nose.
- By inhibiting the action of histamine at the H1 receptors, diphenylpyraline helps alleviate these allergy symptoms.
- Sedative Effects:
- Diphenylpyraline can cross the blood-brain barrier, leading to central nervous system effects.
- This may result in sedation, making it useful for treating conditions that benefit from a sedative effect, such as allergies that interfere with sleep.
- Antimuscarinic Effects:
- Like other first-generation antihistamines, diphenylpyraline may have antimuscarinic (anticholinergic) effects.
- These effects can contribute to side effects such as dry mouth and blurred vision.
Properties and uses:
Diphenylpyraline hydrochloride is a white powder, soluble in water and ethanol, practically insoluble in ether. It is structurally related to diphenhydramine with the aminoalkyl side chain incorporated in a piperidine ring. It is a potent antihistaminic agent.
Dose:
The usual oral dose for adults is 5 mg twice daily.