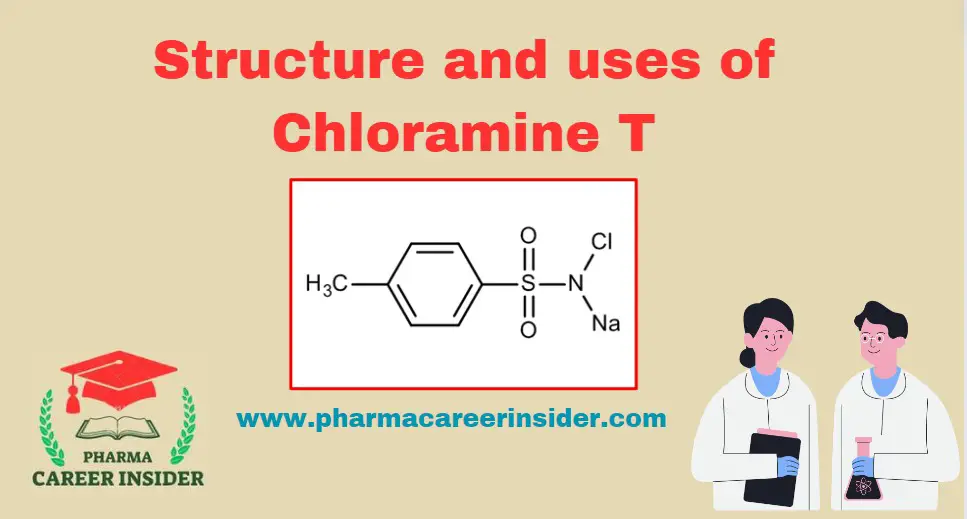
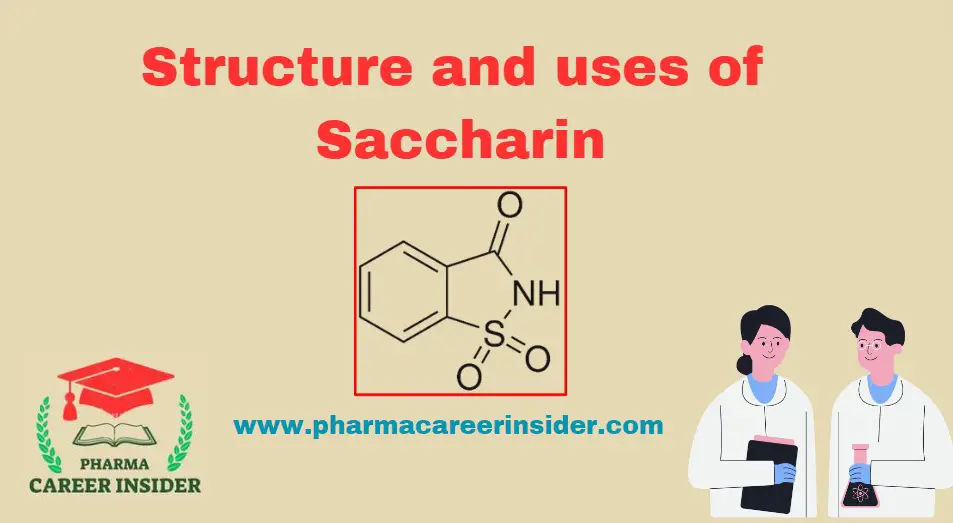
Skin: Structure, Functions
The skin, also known as the integumentary system, is the largest organ in the human body. It is a protective barrier between the internal organs and the external environment. The skin has several layers, each with specific functions. Here’s a detailed note on the structure and functions of the skin: Structure of the Skin 1. … Read more