Chlorination of Benzene
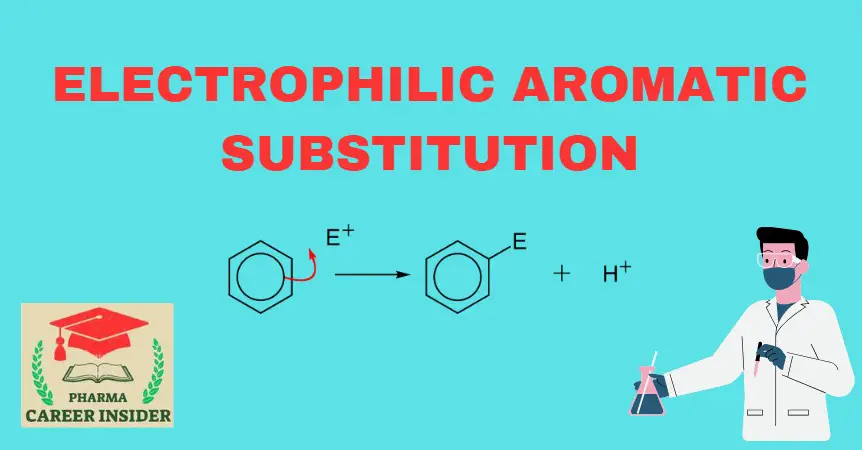
Introduction: The chlorination of benzene involves the introduction of a chlorine atom onto the benzene ring through electrophilic aromatic substitution. A Lewis acid typically catalyzes the reaction, often iron (III) chloride (FeCl3). Here is the reaction with a concise explanation: Here is a step-by-step mechanism for the chlorination of benzene: Step 1: Formation of electrophile: … Read more