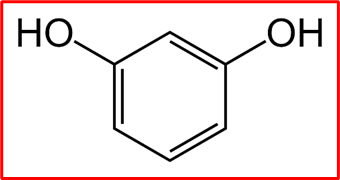
Resorcinol, or m-dihydroxy benzene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H6O2. Its molecular structure consists of a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups attached at the meta position.
Uses of Resorcinol:
1. Resins and Adhesives:
– Resorcinol is a key component in the production of resins, particularly resorcinol-formaldehyde resins, which are used in wood bonding and plywood.
2. Dermatological Applications:
– Resorcinol is used in dermatology for its keratolytic and antiseptic properties. It is found in topical medications for treating various skin conditions, including acne and psoriasis.
3. Hair Dyes:
– It is used in the formulation of hair dyes and colorants.
4. Rubber Industry:
– Resorcinol is used in the rubber industry for the production of resorcinol-formaldehyde-latex (RFL) adhesives, which are employed in the bonding of rubber to textiles in tire manufacturing.
5. Analytical Chemistry:
– Resorcinol is used in analytical chemistry as a reagent for detecting and quantifying certain compounds, including sugars.
6. Photographic Chemicals:
– It has been used historically in the development of certain photographic chemicals.
7. Medicinal Applications:
– In the past, resorcinol has been used in medicinal applications, but its use is limited due to its potential toxicity.
8. Haircare Products:
– Resorcinol is sometimes found in haircare products, particularly those designed for treating scalp conditions.
9. Flavour and Fragrance Industry:
– Resorcinol is employed in the flavour and fragrance industry for its aromatic properties.
10. Chemical Intermediates:
– It serves as an intermediate in synthesizing various chemicals and pharmaceuticals.




