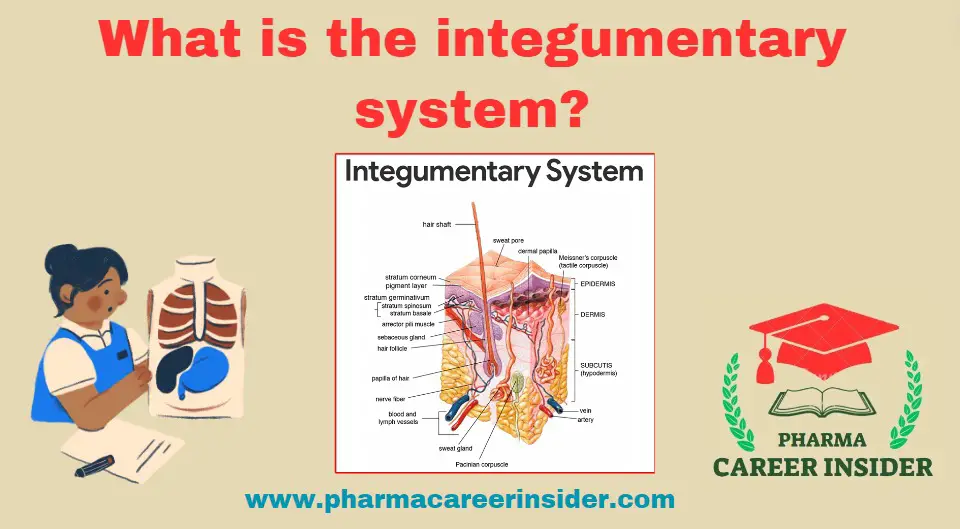
The integumentary system is the organ system that includes the skin, hair, nails, and associated glands. It is the body’s outermost covering and serves as a protective barrier against external factors such as pathogens, UV radiation, and physical injuries.
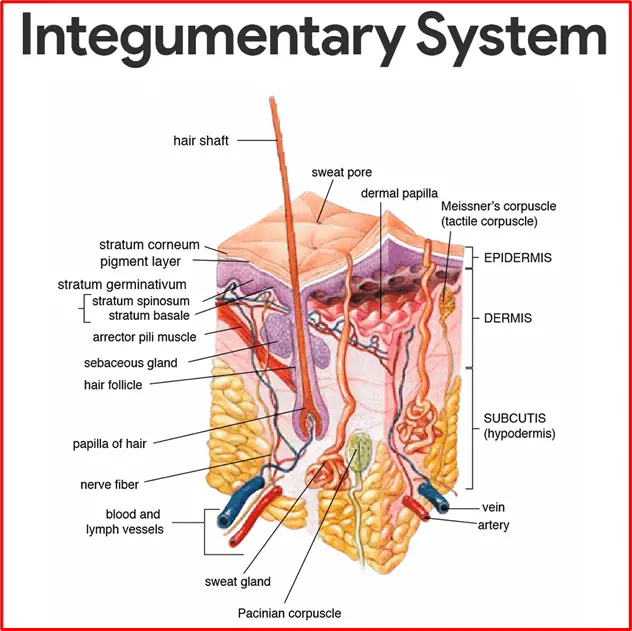
The integumentary system has several key functions:
1. Protection: The skin acts as a protective barrier, shielding the internal organs and tissues from physical damage, pathogens, and harmful substances.
2. Thermoregulation: The system helps regulate body temperature through sweating and dilation or constricting blood vessels in the skin.
3. Sensation: The skin contains various sensory receptors that detect touch, pressure, temperature, and pain.
4. Excretion: Small amounts of waste products, such as salts and water, are eliminated through sweat glands in the skin.
5. Vitamin D Synthesis: The skin plays a crucial role in synthesizing vitamin D when exposed to sunlight, which is essential for calcium absorption and bone health.
6. Immune Defense: The skin is part of the body’s immune defense by preventing pathogens from entering the body and hosting immune cells that respond to infections.
The integumentary system is a complex and dynamic system that plays a vital role in maintaining the overall health and homeostasis of the body.